Every firm requires a powerful instrument like company policy to succeed. They are more than just paperwork or recommendations; they are the roadmap for any business’s success.
Imagine cooking a dish without a recipe That’s what it’s like to manage a firm without the right corporate policies. These policies aid in the establishment of acceptable behavior, clarifying the company’s expectations, and providing a road map for operations.
Creating a company policy, on the other hand, is not a one-size-fits-all approach. It needs careful planning, open communication, and constant updates. In this article we will look at the importance and meaning of corporate policies as well as learn about all the possible policies your business needs in 2023. Let’s start!
Table Of Content
- What is a Company Policy?
- What is the Importance of Company Policy?
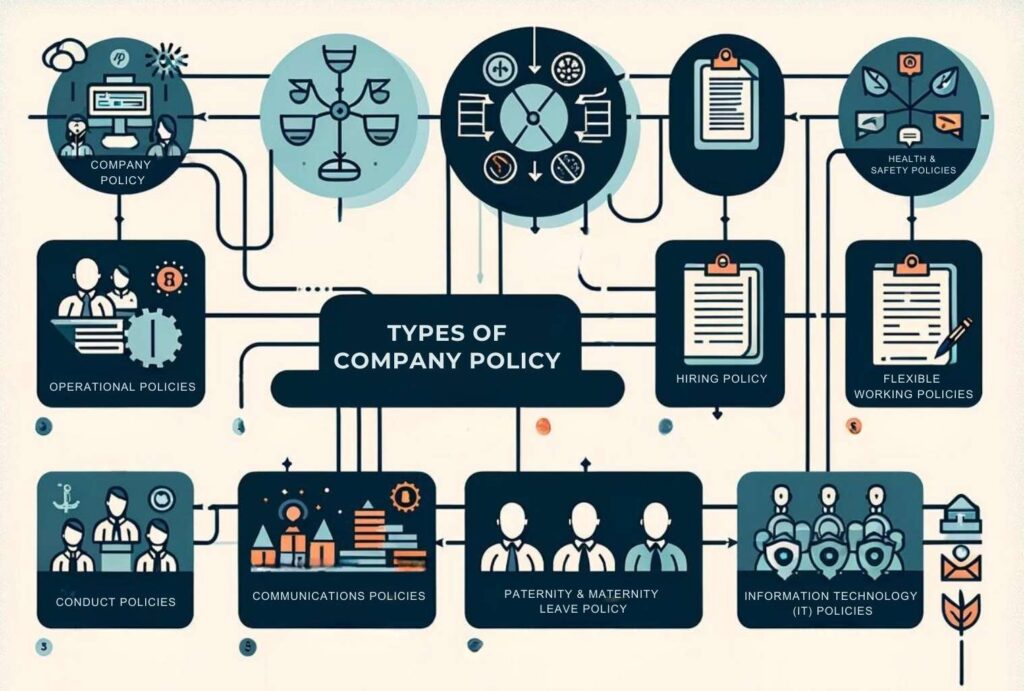
- Types of Company Policies
- 1) Human Resource Policies
- 2) Conduct Policies
- 3) Health and Safety Policies
- 4) Operational Policies
- 5) Information Technology (IT) Policies
- 6) Legal Compliance Policies
- 7) Communications Policies
- 8) Flexible Working Policies
- 9) Sustainability and Environmental Policies
- Tips to Create a Company Policy
What is a Company Policy?
A company policy is a well-defined set of rules and standards that govern how a company works and how employees are supposed to behave at work. It is simply a plan of action, providing a clear, common knowledge of what is and is not acceptable.
These company policies are intended to provide a consistent, fair, and efficient framework for all business-related actions. They can include, but are not limited to, workplace safety, dress requirements, the usage of business property, anti-discrimination and harassment, conflict resolution, and data privacy. It is more than just a set of regulations; it is an important part of defining the company’s identity, values, and standards.
What is the Importance of Company Policy?
Types and Examples of Company Policies
Human Resource Policies
Human resource (HR) policies are explicit rules that organizations adopt to manage and regulate their human resources. These rules specify the employer’s obligations as well as the employees’ rights, responsibilities, and workplace behavior.
They include a wide variety of topics such as hiring, salary, performance management, training and development, health and safety, privacy, and diversity and inclusion. Such rules aid in the establishment of a uniform, fair, and compliant approach to human resource management, making sure all employees are treated fairly.
1) Hiring Policy
 Hiring policy is a set of criteria that an organization follows during the hiring and selection process. This policy is intended to provide a fair, consistent, and transparent procedure while adhering to all applicable employment rules and regulations.
Hiring policy is a set of criteria that an organization follows during the hiring and selection process. This policy is intended to provide a fair, consistent, and transparent procedure while adhering to all applicable employment rules and regulations.
A clear, fair, and efficient recruiting policy can improve an organization’s reputation and make it more appealing to potential employees. This company policy may also include processes for onboarding new employees to ensure they are effectively incorporated into the organization and set up for success from the outset.
2) Employee Handbook
 An employee handbook commonly referred to as an employee manual or staff handbook, is a document that outlines a company’s regulations, policies, and employee expectations. It also specifies what employees can anticipate from the company. It provides a simple guide to the company’s rules and practices, as well as an outline of management’s expectations.
An employee handbook commonly referred to as an employee manual or staff handbook, is a document that outlines a company’s regulations, policies, and employee expectations. It also specifies what employees can anticipate from the company. It provides a simple guide to the company’s rules and practices, as well as an outline of management’s expectations.
3) Employee Wages
 Employee payroll is a critical component of employee management. Employee Wages Policy in India is heavily impacted by the Indian government’s statutory rules and regulations. This policy oversees employee pay and benefits, thereby ensuring a fair and equitable work environment.
Employee payroll is a critical component of employee management. Employee Wages Policy in India is heavily impacted by the Indian government’s statutory rules and regulations. This policy oversees employee pay and benefits, thereby ensuring a fair and equitable work environment.
Wage and salary rules in India are designed to ensure that employees are fairly compensated for their efforts. The Payment of Wages Act, 1936, the Minimum Wage Act, 1948, the Payment of Bonus Act, 1965, and the Equal Remuneration Act, 1976 were merged and simplified by the Code on Wages, 2019 Act.
The Employee Provident Fund & Miscellaneous Provisions Act of 1952 mandates mandatory contributions to the (EPF) from both employers and employees. It is a retirement benefit program that provides a safety net for workers in factories and other organizations. Employees at specified establishments are entitled to gratuity payments upon retirement or termination under the Gratuity Act if they have completed a minimum of five years of continuous employment.
4) Paternity and Maternity Leave Policy
 The Maternity Benefit Act, 1961, which was revised in 2017, mandates maternity leave in India. This Act provides a woman with 26 weeks of compensated maternity leave for her first two children. The leave period is 12 weeks for families with more than two children.
The Maternity Benefit Act, 1961, which was revised in 2017, mandates maternity leave in India. This Act provides a woman with 26 weeks of compensated maternity leave for her first two children. The leave period is 12 weeks for families with more than two children.
The Act compels employers of bigger companies (50 or more employees) to provide creche facilities and, depending on the nature of the employment, allows for work from home after maternity leave. While there is no universal regulatory requirement for paternity leave in India as of September 2021, several government sectors provide male employees with 15 days of paternity vacation.
Here’s what you should do when formulating a maternity and paternity leave company policy. First, clarify the aim of the policy while developing a maternity and paternity leave policy. Following that, describe the qualifying requirements, terms of leave, and the process for requesting leave. Ensure that the policy is in accordance with applicable legislation, and provide a route of communication for employee inquiries.
5) Leave Policy
 In India, a number of regulations govern leave policies, ensuring that workers have a balance between their personal and professional lives. In order to balance work and personal life, take time off, and prevent burnout, leave rules are crucial. They play a critical role in fostering workplace happiness, productivity, and staff retention.
In India, a number of regulations govern leave policies, ensuring that workers have a balance between their personal and professional lives. In order to balance work and personal life, take time off, and prevent burnout, leave rules are crucial. They play a critical role in fostering workplace happiness, productivity, and staff retention.
According to the Factories Act of 1948, an adult employee is entitled to one day of paid yearly leave for every 20 days worked. The Shops and Establishments Act grants employees a minimum of 15 days of earned leave, 12 days of unpaid leave, and 12 days of sick leave annually, while specifics vary from state to state.
Depending on the state’s unique legislation, an employee may be granted a certain amount of public holidays. Employees typically have a right to a minimum of three national holidays under the National and Festival Holidays Act.
When drafting a leave policy, clarify the goal, the sorts of leaves, the amount of leaves permitted, the procedure for applying for leaves, as well as any additional guidelines when establishing a leave policy. Assure that the policy complies with applicable legislation and outline a clear procedure for employees to submit questions.
6) Overtime Policy
 Different labor rules govern India’s overtime policy, ensuring that workers are fairly compensated for the extra hours they put in. No adult worker may be made to work in a factory for more than nine hours on any given day or for more than forty-eight hours on any given week, according to the Factories Act. Any employee who works longer than this is deemed to be doing overtime, and they should be paid double what they would normally be paid.
Different labor rules govern India’s overtime policy, ensuring that workers are fairly compensated for the extra hours they put in. No adult worker may be made to work in a factory for more than nine hours on any given day or for more than forty-eight hours on any given week, according to the Factories Act. Any employee who works longer than this is deemed to be doing overtime, and they should be paid double what they would normally be paid.
The company’s overtime policy must be clear about each employee’s reporting time, working hours, and any policies regarding leaves of absence and holidays. The HR policy must also include the company’s compensation policy for any overtime work performed by any employee.
7) Employee Referral Policy
 Policies for employee referrals are essential for expediting recruitment procedures and saving time and money. Defining a referral policy’s scope and purpose is the first step in creating a successful one. Who can participate, how to submit referrals, rewards for successful referrals, and any other criteria that may apply should all be clearly outlined in the policy.
Policies for employee referrals are essential for expediting recruitment procedures and saving time and money. Defining a referral policy’s scope and purpose is the first step in creating a successful one. Who can participate, how to submit referrals, rewards for successful referrals, and any other criteria that may apply should all be clearly outlined in the policy.
Making sure the policy is transparent and equitable is crucial. Employee referral programs are not specifically regulated in India by any specific law or Act but are frequently used by businesses as a recruitment tactic.
8) Performance Management and Appraisal
 Any firm can benefit from an effective performance management and appraisal policy. To remain effective and relevant, it takes careful planning, clear communication, and regular reassessment.
Any firm can benefit from an effective performance management and appraisal policy. To remain effective and relevant, it takes careful planning, clear communication, and regular reassessment.
In each organization, management must include both performance management and appraisal. These methods not only assess workers’ job performance but also aid in their professional growth and the organization’s overall success.
Performance reviews can be conducted in a variety of ways, such as the 360-degree feedback method, which includes a self-evaluation and input from an employee’s superiors, coworkers, and supervisor. The Management by Objectives (MBO) approach entails establishing clear, quantifiable objectives for the employee to meet within a predetermined time frame. Behavior “anchors” are used as performance indicators in the Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS) technique.
9) Exit Interview Policy
 An exit interview policy is a critical HR tool for understanding the viewpoints of departing employees. While there are no specific regulations in India that govern exit interviews, there are various legal concepts and broader labor rules that must be followed. This protects the rights of both the employer and the departing employee.
An exit interview policy is a critical HR tool for understanding the viewpoints of departing employees. While there are no specific regulations in India that govern exit interviews, there are various legal concepts and broader labor rules that must be followed. This protects the rights of both the employer and the departing employee.
Exit interviews have a defined format and can be done in a variety of ways. Face-to-face meetings, phone interviews, or written questionnaires can be used, as can more modern methods like as internet surveys. The approach chosen is determined by the organization’s size, operational structure, and resources.
10) Employment Termination Policy
 In India, an Employment Termination Policy is a collection of guidelines developed by an organization to handle the process of terminating an employee’s employment. These recommendations outline the conditions for terminating an employment contract as well as the procedures that must be followed during the termination process.
In India, an Employment Termination Policy is a collection of guidelines developed by an organization to handle the process of terminating an employee’s employment. These recommendations outline the conditions for terminating an employment contract as well as the procedures that must be followed during the termination process.
While there is no unifying termination policy law in India, the termination process is governed by a number of labor regulations, including the Industrial Disputes Act of 1947, the Shops and Establishments Act (which varies by state), and the Payment of Gratuity Act of 1972, among others. Regular evaluation and compliance with applicable labor regulations are required to ensure an ethical and successful termination procedure.
Conduct Policies
11) Code of Conduct
 A code of conduct company policy specifies the appropriate behavior that employees are expected to exhibit in the workplace towards their coworkers, supervisors, and the company as a whole. The policy should clearly express desired behaviors, company culture, and the ramifications of code violations. It should be simple to grasp and available to all staff.
A code of conduct company policy specifies the appropriate behavior that employees are expected to exhibit in the workplace towards their coworkers, supervisors, and the company as a whole. The policy should clearly express desired behaviors, company culture, and the ramifications of code violations. It should be simple to grasp and available to all staff.
While there is no explicit law in India that requires a Code of Conduct, multiple acts control various components of it. For instance, the Prevention of Sexual Harassment (POSH) Act of 2013 requires businesses to prevent and address sexual harassment. Consequently, it is critical that such elements be included in the Code of Conduct. Furthermore, organizations must also follow the Companies Act of 2013, which encourages transparency, accountability, and ethical behavior.
A well-written Code of Conduct displays an organization’s dedication to ethical business practises, which can boost its reputation and earn the trust of customers, partners, and the general public.
12) Non-discrimination Policy
 A non-discrimination policy is a key document that protects workplace equity and fairness. It states that no employee or job applicant shall be treated unfairly because of their race, gender, religion, caste, age, disability, or any other protected trait.
A non-discrimination policy is a key document that protects workplace equity and fairness. It states that no employee or job applicant shall be treated unfairly because of their race, gender, religion, caste, age, disability, or any other protected trait.
The Equal Remuneration Act of 1976 outlaws wage discrimination based on gender. Individuals with disabilities are protected from discrimination by the Persons with Disabilities Act of 1995 and the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act of 2016.
Employees have the right to a fair and equal work environment under a non-discrimination policy. They must also respect the rights of their coworkers and follow the policy. Employers are obligated to ensure the policy is upheld, handle complaints promptly and impartially, and protect those who report discrimination from retaliation.
13) Anti Bullying Policy
 An anti-bullying policy establishes a framework for preventing and dealing with bullying, as well as creating a respectful and constructive work environment. It helps to prevent conflict and boost employee morale and productivity by setting the tone for workplace culture.
An anti-bullying policy establishes a framework for preventing and dealing with bullying, as well as creating a respectful and constructive work environment. It helps to prevent conflict and boost employee morale and productivity by setting the tone for workplace culture.
The importance of such a policy goes beyond legal consequences because it can create a toxic work environment, hurting employee mental health and productivity.
Depending on the nature of the bullying behavior, various provisions of the IPC can be invoked in cases of workplace bullying. Sections relating to criminal intimidation (Section 503), insult with intent to cause breach of peace (Section 504), and act threatening life or personal safety of others (Section 336), for example, may be applicable in such circumstances.
14) Sexual Harassment Workplace Policy
 Sexual Harassment Workplace Policy in India is an absolute necessity and correct implementation can considerably help to the formation of a safer, more dignified work environment. It is about creating a respectful culture in which every employee is respected, safeguarded, and treated with dignity.
Sexual Harassment Workplace Policy in India is an absolute necessity and correct implementation can considerably help to the formation of a safer, more dignified work environment. It is about creating a respectful culture in which every employee is respected, safeguarded, and treated with dignity.
The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act, 2013, is India’s primary law covering workplace sexual harassment. It requires all businesses to take steps to avoid sexual harassment, such as establishing an Internal Complaints Committee (ICC) in workplaces with ten or more employees. Employers must also report to the District Officer and, in the case of a corporation, to the Registrar of Companies (ROC) on the number of complaints submitted and their disposal.
Training on workplace behavior is essential for informing employees on what constitutes sexual harassment and the consequences of such behavior. This company policy is not only legally required, but it is also critical for maintaining a respectful and secure workplace.
15) Dress Code Policy
 Maintaining a focused, respectful, and professional work atmosphere requires a dress code policy. In some businesses, it can also be used to enhance safety because it helps set moral and professional standards. The right of employers to impose acceptable dress standards in accordance with the needs and requirements of the business exists in India, despite the lack of formal legislation governing dress codes in the workplace.
Maintaining a focused, respectful, and professional work atmosphere requires a dress code policy. In some businesses, it can also be used to enhance safety because it helps set moral and professional standards. The right of employers to impose acceptable dress standards in accordance with the needs and requirements of the business exists in India, despite the lack of formal legislation governing dress codes in the workplace.
Any required attire must abide by standard labour rules and constitutional clauses. According to Article 14 of the Indian Constitution and other anti-discrimination regulations, it shouldn’t, for instance, discriminate against people based on their gender, religion, caste, or any other protected characteristics.
Creating a Dress Code Policy requires clarity on what is considered appropriate and professional attire in the context of your organization’s culture and industry. It should define standards for both formal and casual dress days and include guidelines for safety gear, if required. The policy should be communicated effectively and sensitively, taking into account the diverse cultural, religious, and personal considerations of employees.
16) Employee Fraternization Policy
 An employee fraternization policy establishes boundaries to control social interactions at work and preserve a professional atmosphere. Employees can better understand what is expected of them and how they should act at work by having access to the company’s fraternization policy. By making sure that personal ties do not jeopardize the standard and integrity of the workplace, it protects both the organization and its employees.
An employee fraternization policy establishes boundaries to control social interactions at work and preserve a professional atmosphere. Employees can better understand what is expected of them and how they should act at work by having access to the company’s fraternization policy. By making sure that personal ties do not jeopardize the standard and integrity of the workplace, it protects both the organization and its employees.
Uncontrolled interactions between coworkers, especially between superiors and subordinates, can result in a number of problems. If fraternization results in conflicts of interest, discomfort, or discrimination, certain legal rules may come into play. If a relationship ends badly, it may result in claims of sexual harassment or a hostile work environment, which could result in legal liabilities.
17) Social Media Policy
 In India, where plenty of industries are doing well, from new startups to traditional manufacturing units, a complete social media policy is essential. While it is encouraged for staff members to represent the firm well online, they are advised not to leak confidential information or get involved in debates that can damage the company’s reputation. This company policy describes acceptable conduct, including sharing private corporate news and events in a responsible manner, as well as restricted conduct, like talking about private information or having defamatory talks. Guidelines for using personal social media during work hours are also included, with the goal of avoiding conflicts of interest and preserving productivity.
In India, where plenty of industries are doing well, from new startups to traditional manufacturing units, a complete social media policy is essential. While it is encouraged for staff members to represent the firm well online, they are advised not to leak confidential information or get involved in debates that can damage the company’s reputation. This company policy describes acceptable conduct, including sharing private corporate news and events in a responsible manner, as well as restricted conduct, like talking about private information or having defamatory talks. Guidelines for using personal social media during work hours are also included, with the goal of avoiding conflicts of interest and preserving productivity.
18) Client Interaction Policy:
 A clear Client Interaction Policy helps keep professional relationships strong and service top-notch. Employees must keep talks strictly professional, avoid conflicts, and be clear and honest. This includes rules for using emails, social media, and online meetings.
A clear Client Interaction Policy helps keep professional relationships strong and service top-notch. Employees must keep talks strictly professional, avoid conflicts, and be clear and honest. This includes rules for using emails, social media, and online meetings.
Different industries need different policies. IT workers focus on tech help, keeping things private, and quick replies. Retail and hospitality stress good customer service and dealing with complaints. Laws like the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, and the Information Technology Act, 2000, make sure businesses treat clients fairly and with respect.
Health and Safety Policies
19) Adaptive Work Culture Policy
The expansion of remote work is one of the most noticeable trends. A catalyst for businesses to embrace work-from-home policies was the COVID-19 epidemic. As a result, thorough instructions for remote work are now frequently included in an Adaptive Work Culture Policy. In 2023, this policy isn’t just a trend, but a necessity. It’s a strategic approach towards creating a resilient, inclusive, and future-ready organization.
20) Media Relations Policy
 A company’s procedures that specify how it communicates with reporters, journalists, and other media professionals are called a media relations company policy. Its goal is to guarantee that all of the company’s interactions with the media are truthful, factual, and represent the goals and values of the organization.
A company’s procedures that specify how it communicates with reporters, journalists, and other media professionals are called a media relations company policy. Its goal is to guarantee that all of the company’s interactions with the media are truthful, factual, and represent the goals and values of the organization.
Usually, it addresses the following important topics:
- Determines who is authorized to speak with the media on the company’s behalf.
- Establishes standards for drafting, authorizing, and disseminating official press releases and statements from companies.
- Outlines particular communication practices to be followed in the event of a crisis or bad press.
- Verifies that all media messages adhere to applicable copyright, defamation, and confidentiality laws.
Operational Policies
21) Attendance And Punctuality Guidelines
 Guidelines for Attendance and Punctuality Any organization’s HR policy must take into account policy in India. It specifies the criteria and requirements the organization has set for employees’ punctuality and attendance at work. The particular requirements for attendance and punctuality may differ in India depending on the type of business, size of the company, and region.
Guidelines for Attendance and Punctuality Any organization’s HR policy must take into account policy in India. It specifies the criteria and requirements the organization has set for employees’ punctuality and attendance at work. The particular requirements for attendance and punctuality may differ in India depending on the type of business, size of the company, and region.
The Factories Act of 1948 and other state-specific Shops and Establishment Acts, which set maximum work hours, overtime rules, and rest breaks, are examples of general labor laws that normally apply to them. In 2023, recording actual hours worked will be more common than rigid attendance regulations due to the growth of remote and flexible employment. For improved tracking and convenience, biometrics are being replaced with cutting-edge software solutions. A greater emphasis is being placed on outputs and productivity rather than actual presence.
Clear communication, training, and regular rule enforcement are all necessary to put the policy into effect. The best managers set an example for their teams and deal with problems swiftly and fairly. Work hours, breaks, leave policies, and the penalty for being late or absent should all be clearly outlined in the policy. All employees should be informed of it, and it should be fair and flexible when possible.
22) Awards and Recognition Policy
 The Awards & Recognition policy aids in talent retention by recognizing employees’ accomplishments. Employees who receive recognition feel valued for their work, which boosts job satisfaction and loyalty and considerably lowers turnover. For staff engagement, motivation, and retention, this policy is essential. It fosters healthy workplace culture, supports positive behavior, and links individual success to organizational objectives. This policy must be updated frequently to be applicable and useful in a workplace that is changing quickly.
The Awards & Recognition policy aids in talent retention by recognizing employees’ accomplishments. Employees who receive recognition feel valued for their work, which boosts job satisfaction and loyalty and considerably lowers turnover. For staff engagement, motivation, and retention, this policy is essential. It fosters healthy workplace culture, supports positive behavior, and links individual success to organizational objectives. This policy must be updated frequently to be applicable and useful in a workplace that is changing quickly.
Peer-to-peer and personalized recognition will be more common in 2023. Instantaneous recognition is now possible thanks to digital platforms, and businesses are incorporating recognition into their regular working procedures. Additionally, non-financial rewards like training opportunities, flexible scheduling, or mental wellness days are popular.
23) Travel Policy
 For company travel to be efficiently managed, a corporate travel policy is essential. It guarantees that staff members are aware of the business’s travel policies, encourages the fair and effective use of resources, and aids in keeping travel expenses under control. The satisfaction of the workforce and the reputation of the business are also impacted by addressing safety, comfort, and sustainability.
For company travel to be efficiently managed, a corporate travel policy is essential. It guarantees that staff members are aware of the business’s travel policies, encourages the fair and effective use of resources, and aids in keeping travel expenses under control. The satisfaction of the workforce and the reputation of the business are also impacted by addressing safety, comfort, and sustainability.
For effective booking and spending tracking, more firms are choosing travel management solutions. Additionally, policies encouraging eco-friendly travel options are gaining popularity. Setting up a transparent and equitable travel policy is essential for the success of your business because ineffective travel expenditure management costs money.
The policy must abide by all relevant regulations, including those governing labor, taxes, and data protection. For overseas travel, it should also be consistent with the Foreign Exchange Management Act of 1999. Guidelines for bookings, allowances, spending reporting, and resolving crises are all crucial criteria. Different travel scenarios, including domestic, foreign, short-term, and long-term, should be covered by the insurance. It ought to be equitable, open, and consistent with the principles and culture of the company.
24) Expenses Reimbursement Policy
 To effectively manage work-related expenses, companies must have an expense reimbursement policy. This policy provides employees with clear standards, ensures fair practices, aids in cost management, and ensures compliance with regulatory obligations. Employees must report expenses truthfully and accurately and are entitled to timely compensation. Conversely, employers must establish clear policies, process reimbursement requests promptly, and maintain ethical standards.
To effectively manage work-related expenses, companies must have an expense reimbursement policy. This policy provides employees with clear standards, ensures fair practices, aids in cost management, and ensures compliance with regulatory obligations. Employees must report expenses truthfully and accurately and are entitled to timely compensation. Conversely, employers must establish clear policies, process reimbursement requests promptly, and maintain ethical standards.
This policy is a crucial tool for creating an open and equitable workplace. It must comply with all relevant labor, tax, and data privacy laws in India. Additionally, it should adhere to the Goods and Services Tax (GST) law to allow for input tax credits. The policy should clearly spell out the reimbursement process, the required level of documentation, deadlines, and the dispute resolution process.
25) Reimbursement Policy For Sales Expenses
In the dynamic world of sales, the Sales Expenses Reimbursement Policy is a cornerstone of business operations. Building trust between the business and its sales staff requires a carefully written Sales Expenses Reimbursement Policy. It offers confidence and transparency, encouraging workers to carry out their responsibilities without worrying about facing financial hardship. Software for managing expenses is becoming widely used in enterprises to improve productivity.
There are no explicit rules in India that deal with reimbursing sales expenditures. However, businesses should abide by more extensive tax and labor requirements. Employees are required to submit expenses honestly and on time and have a claim to reimbursement for legitimate work-related expenses. As an employer, you are required to set clear rules, handle refunds quickly, and support ethical behavior.
26) Cash Handling Policy
Information Technology (IT) Policies
27) Employee Cell Phone Policy
 Establishing rules for mobile phone usage inside of a business is the primary goal of establishing an employee phone policy. It is a road plan for navigating the area where work and technology converge, encouraging a climate at work that is efficient, civil, and consistent with the law. Its excessive use, however, can divert workers and employees. The appropriate and inappropriate usage of phones in a company must therefore be taken into account.
Establishing rules for mobile phone usage inside of a business is the primary goal of establishing an employee phone policy. It is a road plan for navigating the area where work and technology converge, encouraging a climate at work that is efficient, civil, and consistent with the law. Its excessive use, however, can divert workers and employees. The appropriate and inappropriate usage of phones in a company must therefore be taken into account.
The Information Technology Act of 2000’s privacy regulations come into play, particularly if companies track their employees’ phone activity. Employers must make sure that their cell phone policies respect their employees’ right to privacy. The acceptable use of cell phones while at work must be specified in the policy in detail. It must emphasize the need of keeping a professional atmosphere, respecting others’ personal space, and making sure the standard of work isn’t compromised. The company policy should cover safety issues including using a mobile device while operating machinery or while driving for work.
28) Company Cell Phone Policy
In essence, a thorough company cell phone policy acts as a key guide for employees, allowing them to make the most use of the company’s technology while adhering to corporate principles, legal obligations, and personal boundaries. The proper adoption of such a program could boost workplace productivity and professionalism dramatically.
The policy should explicitly state what uses of company-provided cell phones are permitted and undesirable. This includes the use of cell phones for personal purposes, data usage standards, and confidentiality and privacy rules. Cell phone rules may need to cover the usage of phones for work and business travel, safety and privacy concerns, and maintaining a productive workplace, depending on the types of occupations your employees undertake.
29) Bring Your Own Device Policy
With the widespread of digitalization, there is a growing trend in workplaces of ‘Bring Your Own Device’ (BYOD). BYOD policies are regulations and standards that allow employees to use their personal devices for work purposes, such as laptops, cellphones, or tablets. Acceptable use, data security, privacy, device administration, and support should all be covered. It must also include mechanisms for data encryption, secure network access, and data breach prevention procedures.
The current increase in remote working culture needs that the policy accommodates WFH settings as well. However, it must be written with legal obligations and probable problems in mind to guarantee a safe and pleasant work environment for your company.
30) Employee Laptop Policy
 Creating a Laptop Policy necessitates balancing an employee’s freedom of use with the company’s need for security. Some of the problems that must be addressed in designing the policy are privacy concerns, data security, device upkeep, and effective utilization.
Creating a Laptop Policy necessitates balancing an employee’s freedom of use with the company’s need for security. Some of the problems that must be addressed in designing the policy are privacy concerns, data security, device upkeep, and effective utilization.
An Employee Laptop Policy is a critical component of a company’s IT policy that defines the guidelines for using company-provided laptop computers. Acceptable use, data security, software installations, device upkeep, and support should all be addressed in the Laptop Policy.
Encryption, regular updates, firewall configuration, and unauthorized access prevention should all be part of data security procedures. It should also emphasize the importance of staff protecting the equipment from loss or damage.
31) Internet And Email Policy For Employees
 An Internet and Email Policy is required for several reasons. By setting up clear guidelines for personnel, it prevents resource waste. It protects the business from potential legal issues and guarantees a secure online environment. Additionally, it helps to protect sensitive data, reduce cyber risks, and maintain the reputation of the business.
An Internet and Email Policy is required for several reasons. By setting up clear guidelines for personnel, it prevents resource waste. It protects the business from potential legal issues and guarantees a secure online environment. Additionally, it helps to protect sensitive data, reduce cyber risks, and maintain the reputation of the business.
The Information Technology Act of 2000 addresses data privacy and cybercrime issues, ensuring that the company’s digital communications are secure and legal. With the rise of cyber dangers, rules must include sections on security practices, such as the use of secure, encrypted connections, the regular upgrading of passwords, and the identification of potential phishing emails or questionable online activity.
32) Company Data Protection Policy
 A Company Data Protection Policy in India is designed to protect sensitive and personal information within the company. Employee information, client databases, financial information, and private research or operational data are all examples of this information.
A Company Data Protection Policy in India is designed to protect sensitive and personal information within the company. Employee information, client databases, financial information, and private research or operational data are all examples of this information.
The policy outlines the rights and obligations of both employees and the corporation, as well as how the organization gathers, saves, processes, and shares data. Challenges such as growing cyber threats, technological developments, and legislative changes make maintaining a flawless system difficult yet necessary. Employees must attend frequent training and awareness seminars to address these difficulties.
33) Anti-Spam Policy
 The Anti-Spam Policy is critical in India for preserving the integrity and productivity of electronic communication channels, particularly email. These regulations are primarily governed by the Information Technology Act of 2000, and more specifically, Section 66A of that Act, which addresses offensive statements sent via communication services.
The Anti-Spam Policy is critical in India for preserving the integrity and productivity of electronic communication channels, particularly email. These regulations are primarily governed by the Information Technology Act of 2000, and more specifically, Section 66A of that Act, which addresses offensive statements sent via communication services.
To begin, companies must develop unambiguous definitions of spam. Spam is typically defined as any unwanted, irrelevant, or inappropriate message transmitted over the internet to a large number of people without their consent. Commercial emails, promotional messages, and bulk emails are examples of this.
Developing an Anti-Spam Policy entails disseminating these definitions and standards to all employees, monitoring compliance, and implementing harsh penalties for infractions. An Anti-Spam company policy is required not just for legal compliance and to avoid penalties, but also for creating trust with clients and consumers and maintaining a polite and ethical communication environment.
34) Website Privacy Policy
A website privacy policy in India serves as a compass for navigating the world of online user data. This crucial legal document outlines how a business collects, makes use of, and handles user data acquired from their website.
The Information Technology Act of 2000 and the IT Rules of 2011 set the guidelines for data management, guaranteeing accountability, openness, and user privacy protection. It becomes a focal point of trust between customers and the business, demonstrating its dedication to protecting customer information in the age of digital transactions and interactions.
Due to the rise in online risks and data breaches, developing a strong website privacy policy has become difficult. Your organization must take into account a number of variables, including their industry, the sort of data they handle, and the platforms they employ.
Businesses need to keep their privacy policies up to date as new technology and user behaviors arise. Companies should first do a data audit to understand the types of data they gather and how it is utilized before developing an effective website privacy policy. Based on this, they may create a thorough policy that is simple to comprehend and conforms with all applicable rules and regulations.
35) Record Maintenance And Confidentiality Policy
 A Record Maintenance and Confidentiality Policy is a vital organizational framework in India in this day and age. It dictates how companies manage, store, and safeguard their data. This company policy is an important component of your company’s strategic and operational infrastructure, assuring both legal compliance and the secure management of sensitive data.
A Record Maintenance and Confidentiality Policy is a vital organizational framework in India in this day and age. It dictates how companies manage, store, and safeguard their data. This company policy is an important component of your company’s strategic and operational infrastructure, assuring both legal compliance and the secure management of sensitive data.
Businesses must strike a balance between ease of access to data and robust security measures to secure sensitive information. Employee records, financial documents, and consumer data, for example, all require specific solutions based on their sensitivity and preservation requirements.
36) Internet Usage Policy:
An Internet Usage Policy sets workplace rules for using the internet and company devices. It protects against online threats, improves focus, prevents legal issues, keeps the internet at a faster pace for work, safeguards the company’s reputation, and secures data. It follows data protection laws, like the IT Act in India, to ensure legal compliance. Monitoring tools and employee training sessions support the policy’s enforcement.
The policy includes:
- What internet activities are allowed and not allowed.
- How to keep company data safe and follow copyright laws.
- Rules for using email, messaging, and browsing at work.
- What happens if someone breaks the rules, from warnings to more serious actions.
Legal Compliance Policies
37) Anti Bribery/Anti Corruption Policy
 In India, an anti-bribery/anti-corruption policy is essential for preventing illegal acts that compromise an organization’s integrity and growth.
In India, an anti-bribery/anti-corruption policy is essential for preventing illegal acts that compromise an organization’s integrity and growth.
Legally, it guarantees adherence to local, state, and, in the case of multinational enterprises, international legislation. In terms of ethics, it promotes honesty, fairness, and integrity at work. Lastly, when it comes to operations, it protects the company’s reputation, which has an effect on customer confidence and corporate success.
Gifts, hospitality, purchasing, sponsorships, donations, and third-party connections should all be covered by this policy. Each organization should also set up a transparent, private reporting system that enables staff to report infractions without fear of retaliation.
38) Intellectual Property Rights Policy:
An Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) Company Policy is a must for protecting a company’s unique and innovative efforts. It establishes clear guidelines for who owns and uses intellectual property, including as patents and copyrights developed by employees. The policy is based on legal guidance to comply with worldwide intellectual property rules, including the use of technologies such as IP management software for tracking IP and employee awareness training programmes.
It promises compliance with laws such as India’s Copyright Act and international treaties like as TRIPS, which protect the company’s and employees’ intellectual property rights around the world. The policy addresses the ownership of intellectual property created at work, standards for its usage, and safeguards against misuse or theft, thereby protecting the company’s important intellectual assets.
39) Equal Employment Opportunity Policy:
An Equal Opportunity Policy in the workplace is designed to ensure fairness and equality, guaranteeing that every employee and applicant is treated equally, without discrimination based on personal characteristics, appearances, beliefs, religion or background. This policy is typically developed with input from HR and legal departments and is supported by training sessions to enhance understanding and implementation. This policy is applicable at all times, guiding daily interactions and decision-making processes in the workplace. It is particularly referenced during recruitment, performance evaluations, promotions, and when addressing complaints or disputes related to discrimination or harassment.
Communications Policies
40) Communications Policy
In the Indian workforce, a communications policy is a set of rules that specify how information should be shared between individuals and groups inside an organization as well as between the organization and outside stakeholders.
Detailing the channels, expectations, and protocol for communication within the organization is part of creating a communications policy. Both internal and external communication are included. The communication obligations, expectations, and potential sanctions for policy violations should all be addressed in the policy.
Although there are no particular rules in India governing workplace communication, other pieces of legislation like the Indian Contract Act of 1872, the Information Technology Act of 2000, and the Companies Act of 2013 have a direct impact on the framework. In order to maintain efficient, polite, and legal communication, employers and employees each have respective rights and obligations.
The policy must take into account the subtleties of virtual communication in the era of remote employment. This policy may include instructions on proper conduct during video conferences. It can also guide professional communication online and how to safeguard data while working remotely. By specifying how employees should communicate, such a policy helps ensure a cordial, effective, and legally compliant office environment.
41) Policy For Media Relations
Companies must adapt to new media and communication technologies in the ever growing digital world. The media relations policy comes into play in this situation. For a company to maintain a positive public image, a strong media relations strategy is essential. It assists in controlling the information flow from the business to the general public, assuring correctness, consistency, and timeliness. Additionally, it aids in shielding the business from potential legal problems brought on by public communication.
A successful media relations strategy can enhance a company’s reputation, gain public favor, and build lasting relationships with media professionals. In India, several laws influence the legal framework for a media relations policy.
Key examples include the SEBI Regulations, which govern communications in listed companies, and especially regarding financial and insider information. Additionally, the Companies Act 2013 requires certain disclosures to shareholders and the general public.
Regarding rules against defamation, the Indian Penal Code (IPC) also holds some significance. Furthermore, when dealing with digital media platforms, conformity to the Information Technology Act, 2000 is essential. Together, these laws primarily make up the legislative framework around which a media relations policy is created and implemented.
Flexible Working Policies
42) Work from Home Policy
 The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly increased the significance of the work from home (WFH) policy. The requirements, obligations, and assistance provided to workers who work remotely are described in this policy. Eligibility, obligations, working conditions, rules for communication, data security, and equipment requirements should all be covered in a WFH policy.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly increased the significance of the work from home (WFH) policy. The requirements, obligations, and assistance provided to workers who work remotely are described in this policy. Eligibility, obligations, working conditions, rules for communication, data security, and equipment requirements should all be covered in a WFH policy.
Effective communication and uniform application of this policy throughout the organization are required. The Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020 emphasizes employers’ obligations to offer a safe work environment, even at home, despite the fact that India lacks specific regulations governing WFH arrangements. Data and privacy protection in remote working arrangements are governed by the Information Technology Act of 2000 and accompanying regulations.
In India in 2023, hybrid work models that combine WFH and in-office employment are becoming more popular. Additionally, employers are paying more attention to their workers’ mental health, offering flexible hours and utilizing cutting-edge technology for seamless remote working. Additionally, there is a greater focus on employee upskilling to help them adjust to the digital workplace.
43) Part-Time Work Policy
A Part-Time Work Company Policy is increasingly crucial today, promoting work-life balance and tapping into a diverse talent pool. It brings operational flexibility, aids in cost management, enhances productivity, and supports employee well-being, making a company more attractive as a progressive workplace.
In India, part-time is typically considered up to 30 hours per week, aligning with the Shops and Establishment Act and the Minimum Wages Act, which set standards for working hours, minimum wages, and more. Adhering to these regulations is key to legal compliance and fair employee treatment. According to a report by the International Labour Organization (ILO), flexible employment policies, including part-time work, are linked to higher job satisfaction and organizational commitment, underscoring their importance in the modern workplace.
Sustainability and Environmental Policies
44) Gifts Entertainment Policy
Maintaining an ethical and legally compliant company environment in India requires adherence to the Gifts and Entertainment Policy. It aids in directing employees’ behavior and guarantees that commercial dealings are carried out with the utmost integrity.
In India, corporate practices related to gifts and entertainment are governed by the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988, and the Companies Act, 2013. The Companies Act mandates businesses to maintain effective internal controls to prevent fraudulent acts. Meanwhile, the Prevention of Corruption Act outlines and criminalizes corrupt practices.
This policy is essential to uphold a company’s reputation as well as legal requirements.
45) Green Office Policy:
A Green Office is about building an environmentally friendly workspace. It’s more than just adding a few plants and turning off the lights. It’s a comprehensive approach to making sure every aspect in the office, from resource usage to thinking, material sourcing, packaging, behavior etc is environmentally friendly. This involves doing a variety of things to ensure that we do not destroy the environment.
A variety of environmental legislation and activities aimed at decreasing carbon footprints and encouraging workplace sustainability are driving the green office trend. They are:
- The Energy Conservation Act of 2001: It encourages energy-efficient methods in office buildings to reduce usage.
- Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA): This system helps offices earn green building certification by assessing their environmental performance.
- The National Building Code of India: This provides rules for sustainable and energy-efficient building construction in offices.
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE): This law promotes energy efficiency in commercial buildings, particularly workplaces, using a star rating system.
Tips to Create a Company Policy:
FAQ’s:
What are company policies, and why are they important?
Company policies are a set of guidelines that dictate how an organization should operate. Also, they define how employees should act or work. These policies ensure consistency and help clarify expectations for everyone involved. Additionally, they protect the business and its people from mistakes or legal issues.
How are company policies in India different from other countries?
Although certain rules might stay the same everywhere, others are designed specifically along the lines of The Indian Constitution and customs of culture. This makes sure that they are suitable for companies working in India.
What are the five common policy statements?
The following five common policy statements actively establish various organizational standards:
1) Code of Conduct sets out desired workplace behaviors
2) Equal Opportunity ensures equality in hiring
3) Health and Safety explains safety procedures
4) Attendance and Leave defines time-off regulations
5) Data Protection specifies how to handle personal and business data.
How often are policies reviewed?
Usually, policies are reviewed once a year. But they can be reviewed and changed more than once depending on changes in laws, business operations, or market trends. Keeping these recommendations current, functional, and compliant with the latest laws, regulations, and commercial best practices is essential. Therefore, it makes sense to conduct annual revisions.
How does the company handle grievances or concerns raised by employees?
Every business or organization usually has a formal grievance process. An employee’s immediate supervisor or an authority can be contacted with such complaints. Each issue is taken very seriously, quickly investigated, and confidentially handled. Fair settlement of issues and building a supportive workplace culture is very important.
How do business policies affect the working environment?
Well-crafted company policies helps you build a healthy work atmosphere. They encourage justice, uniformity, and clear guidelines, which can lead to higher morale and performance.
What should be part of a corporate policy?
Health and safety, equal opportunity, code of conduct, leave of absence, and disciplinary action are all subjects that company rules should address. They should be straightforward, thorough, and easily available to all employees.
Conclusion
Lastly, the significance of organized company policies in India cannot be emphasized. High-performing firms understand the fundamental link between well-crafted policies and increasing sales. In our dynamic business world, the regulatory landscape and industry-specific standards are growing. Developing these policies from the start could be a demanding process.
That is why, using professionally developed, pre-made company policy documents might be game changer. These templates are created by industry specialists. They ensure that all relevant issues are addressed. This saves time and improves policy comprehension.
They offer a solid foundation that can be adjusted to your company’s needs. Smart Sales Kit can be just the right choice. Head on to our website to know more about the sales kit’s features!

 An Adaptive Work Culture Policy is crucial for fostering a flexible, inclusive, and supportive work environment. This type of environment is adept at adjusting to changing business conditions. In India, this is particularly important due to the diversity of its workforce.
An Adaptive Work Culture Policy is crucial for fostering a flexible, inclusive, and supportive work environment. This type of environment is adept at adjusting to changing business conditions. In India, this is particularly important due to the diversity of its workforce. A cash handling policy in a firm or organization consists of rules and procedures for managing and controlling cash or its equivalents. This includes handling, receiving, storing, and depositing cash. The primary objectives of this policy are to protect cash transactions, minimize the risk of theft, fraud, or human error, and maintain an audit trail for transparency and accountability.
A cash handling policy in a firm or organization consists of rules and procedures for managing and controlling cash or its equivalents. This includes handling, receiving, storing, and depositing cash. The primary objectives of this policy are to protect cash transactions, minimize the risk of theft, fraud, or human error, and maintain an audit trail for transparency and accountability.

One Comment