 HR policies are super important for any business in India, but they’re often forgotten when you’re just starting out or running a small startup. As your team gets bigger, managing everyone fairly becomes a bigger challenge. Every business, no matter how big or small, needs good HR policies to keep things running smoothly.
HR policies are super important for any business in India, but they’re often forgotten when you’re just starting out or running a small startup. As your team gets bigger, managing everyone fairly becomes a bigger challenge. Every business, no matter how big or small, needs good HR policies to keep things running smoothly.
In this blog, we’re going to show you why HR policies in India are more than just rules. They help make your workplace safe and positive. We’ll also give you a list of 45 must-have HR policies for companies in India.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
What are HR Policies?
Types of HR Policies
Importance of HR Policies in India
List of 45 HR Policies in India
- Compliance Policies
- Compensation and Benefits Policies
- Workplace Safety and Health Policies
- Employee Conduct Policies
- Data and Information Security Policies
- Recruitment and Termination Policies
- Work-Life Balance Policies
What are HR Policies?
HR policies in India are the regulations and guidelines that companies and employees must go by in order to maintain a peaceful and effective workplace. They prevent misunderstandings and maintain a healthy work atmosphere by being open, fair, and honest and making sure that everyone is in sync.
The reason this is important is because HR policies in India make sure that everyone is treated fairly, a level of trust can be maintained, and it even has the power to turn your business into an exciting place to work.
Additionally, they can keep you safe simply by making sure that you follow the law, particularly when it comes to important matters like health and safety. Therefore, even though HR policies can look like a lot of paperwork, doing them correctly may truly set your company up for success.
Types of HR Policies in India
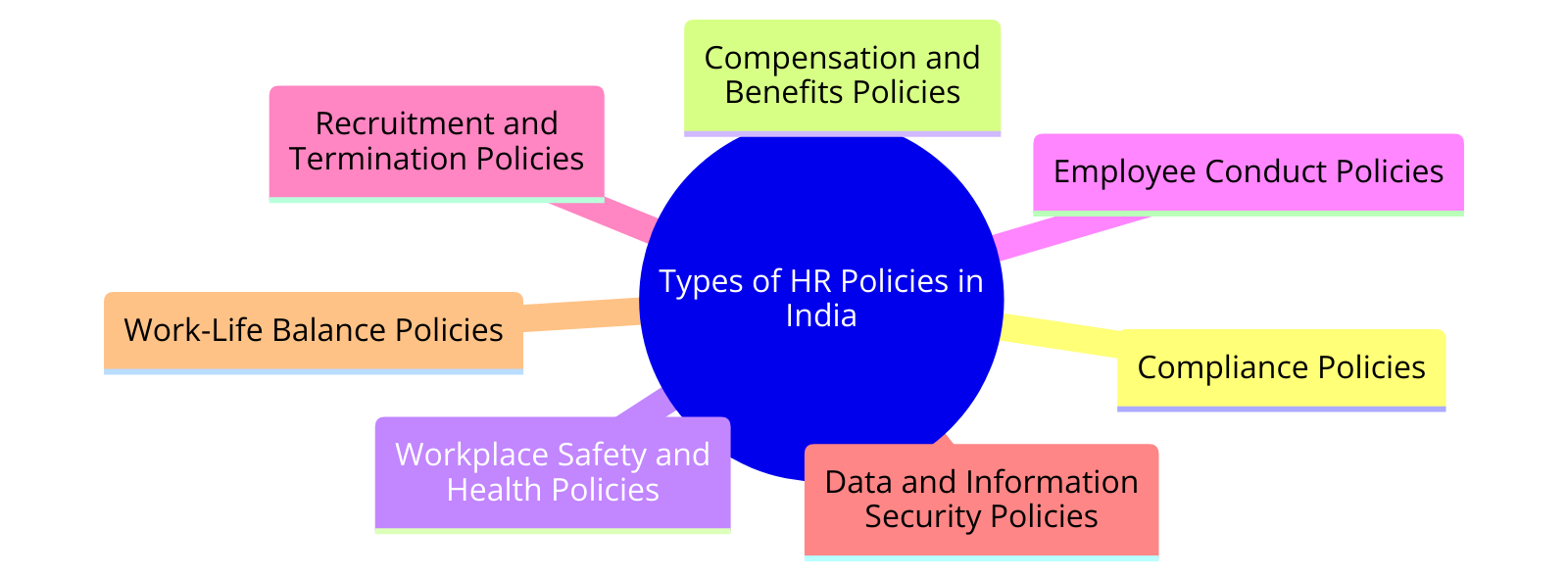
Importance of HR Policies in India
HR policies in India have a significant impact on how the work place grows, matching the values and culture of the company. Employers and employees have their rights and obligations clearly defined, which creates a positive and effective work environment. HR policies in India are necessary for:
- Clarity: Gives precise instructions on policies and expectations inside the company.
- Employee Engagement: Promotes fairness and openness to increase employee happiness and satisfaction.
- Conflict Resolution: Provides an organised method for settling disagreements at work.
- Performance Management: Enables fair assessment and staff growth.
- Legal Compliance: Helps businesses in following labor laws and rules.
- Risk Management: Reduces legal risks and shield the company from potential lawsuits.
Not just as a broad concept but HR policies in India can prove to be useful in day-to-day instances at work too. For example, an employee feels they’ve been unfairly treated/discriminated against at their workplace.
In such a situation, the Anti-Discrimination Policy as well as the Grievance Handling Policy can provide a framework for solving these concerns, making sure the employee’s voice is heard and appropriate measures are taken. This not only helps in maintaining fairness but also reinforces the company’s commitment to employee welfare.
List Of 45 HR Policies In India
Having a comprehensive list of HR policies helps in maintaining your company’s integrity, enhancing employee satisfaction, and being mindful of any legal risks. Here is the list of 25 HR Policies in India:
*Disclaimer- The following list is not arranged in any particular order
Compliance Policies:
1) Anti Bribery/Anti Corruption Policy
2) Sexual Harassment in The Workplace Policy
3) Corporate Social Responsibility Policy
4) Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO)
5) Anti-Discrimination Policy
6) Whistleblower Policy
7) Drug and Alcohol Policy
Compensation and Benefits Policies:
8) Maternity Leave Policy
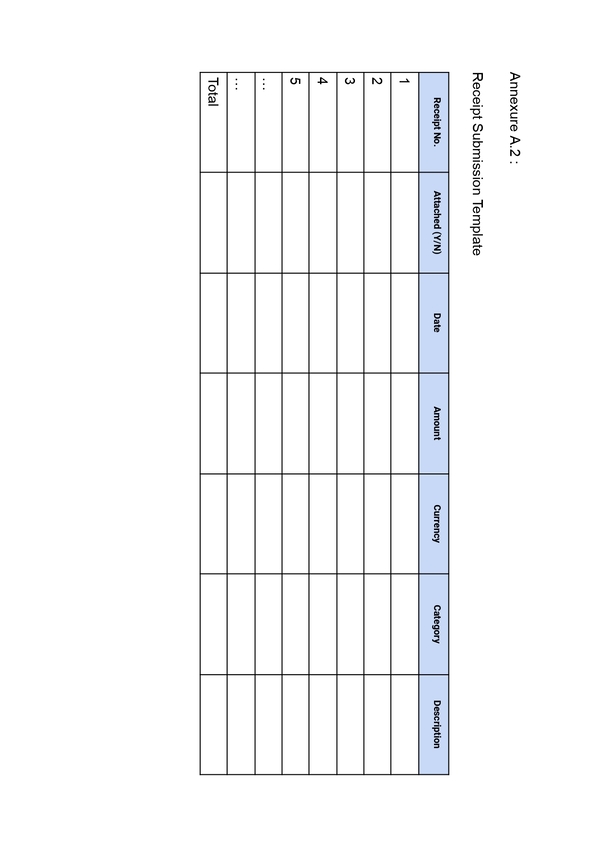
9) Expenses Reimbursement Policy
10) Overtime Policy
11) Sales Commission Policy
12) Employee Provident Fund Policy
13) Employee Wages Policy
14) Compensation and Benefits Policy
15) Gratuity Policy
16) Grievance Handling Policy
Workplace Safety and Health Policies:
17) Health and Safety Policy
18) Workplace Violence Prevention Policy
19) Hybrid Work Model Policy
Employee Conduct Policies:
20) Anti Bullying Policy
21) Attendance And Punctuality Guidelines
22) Dress Code Policy
23) Employee Gift Policy
24) Code of Conduct
25) Social Media Policy
26) Menstrual Leave Policy
Data and Information Security Policies:
27) Company Data Protection Policy
28) Record Maintenance And Confidentiality Policy
29) Internet And Email Policy For Employees
30) Laptop Policy
31) Employee Privacy Policy
32) Anti-Spam Policy
Recruitment and Termination Policies:
33) Employee Referral Program Policy
34) Exit Interview Policy
35) Recruitment and Hiring Policy
36) Termination and Separation Policy
37) Probation and Confirmation Policy
38) Employee Onboarding and Offboarding Policy
39) Employment Contracts/Agreement
40) Non-Compete and Non-Solicitation Policy
Work-Life Balance Policies:
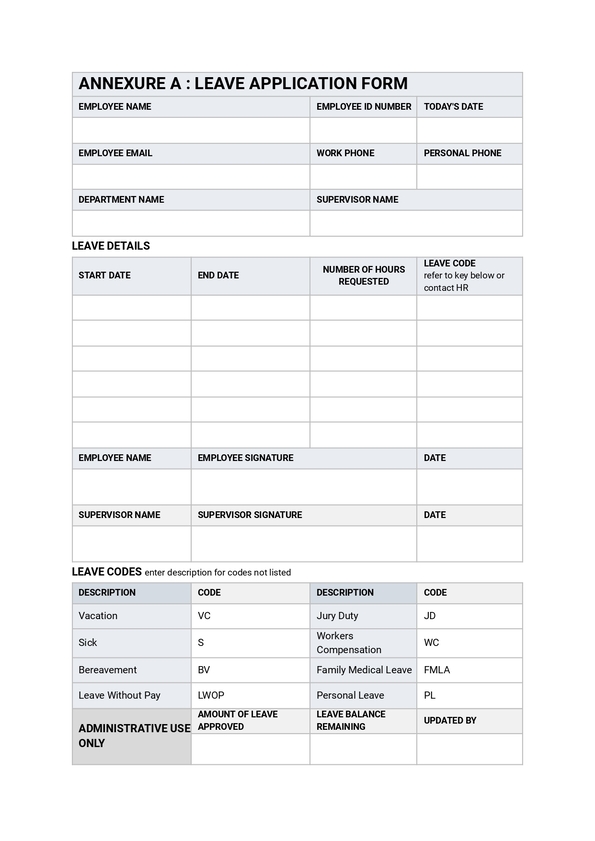
41) Leave and Attendance Policy
42) Remote Work Policy
43) Menstrual Leave Policy
44) Employee Development and Training Policy
45) Employee Recognition Policy
Compliance Policies:
1) Anti Bribery/Anti Corruption Policy
 Under India’s modified Prevention of Corruption Act (POCA), both individuals as well as companies involved in bribery face harsh punishments. Bribery, for example, can result in a seven-year prison sentence. And businesses that offer bribes or are involved in any kind of corruption can face penalties, as well as imprisonment and fines for top employees.
Under India’s modified Prevention of Corruption Act (POCA), both individuals as well as companies involved in bribery face harsh punishments. Bribery, for example, can result in a seven-year prison sentence. And businesses that offer bribes or are involved in any kind of corruption can face penalties, as well as imprisonment and fines for top employees.
In the corporate sector, unethical practices such as embezzlement and accepting bribes for being preferred over others still exist. Hence, Human Resource policies like this play a pivotal role in limiting this by educating employees on ethical standards and establishing clear methods for reporting such behaviour.
2) Sexual Harassment in The Workplace Policy
 Sexual harassment at the workplace includes unwelcome sexual behavior, like inappropriate advances, requests for favors, or any verbal or physical act of a sexual nature that creates a hostile work environment. This can occur in person or online and affects all genders. To report such incidents, employees should approach their HR department, which follows the guidelines set by India’s 2013 act on sexual harassment.
Sexual harassment at the workplace includes unwelcome sexual behavior, like inappropriate advances, requests for favors, or any verbal or physical act of a sexual nature that creates a hostile work environment. This can occur in person or online and affects all genders. To report such incidents, employees should approach their HR department, which follows the guidelines set by India’s 2013 act on sexual harassment.
The penalties for proven harassment cases, as per the 2013 POSH Rules, can range from formal apologies and written warnings to more severe actions like termination or even heavy fines. These HR policies in India create a safe work environment, free from harassment, and holds offenders accountable for their actions.
3) Corporate Social Responsibility Policy
 Under Section 135 of the Companies Act of 2013, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has become a legal mandate for a number of businesses, in addition to being an independent idea for all to contribute to social and environmental progress. This law requires businesses that meet certain financial standards, such as net worth over Rs. 500 crore, turnover over Rs. 1000 crore, or net profit over Rs. 5 crore, to contribute at least 2% of their average net profits over the previous three fiscal years to corporate social responsibility initiatives. These can include any program that the company’s CSR Committee advises that complies with the Act’s criteria, as well as programs included in Schedule VII of the Act, which covers rural development, healthcare, education, and environmental sustainability.
Under Section 135 of the Companies Act of 2013, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has become a legal mandate for a number of businesses, in addition to being an independent idea for all to contribute to social and environmental progress. This law requires businesses that meet certain financial standards, such as net worth over Rs. 500 crore, turnover over Rs. 1000 crore, or net profit over Rs. 5 crore, to contribute at least 2% of their average net profits over the previous three fiscal years to corporate social responsibility initiatives. These can include any program that the company’s CSR Committee advises that complies with the Act’s criteria, as well as programs included in Schedule VII of the Act, which covers rural development, healthcare, education, and environmental sustainability.
4) Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO)
 In India, the Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) HR policy ensures everyone gets a fair chance at jobs and promotions, regardless of their background. This idea is backed by India’s Constitution, especially Article 16, which says no one can be discriminated against because of their religion, race, caste, sex, or where they were born when it comes to jobs. This means companies must follow EEO rules, making sure job decisions are based on what someone can do, not who they are. EEO isn’t just for hiring; it’s a rule that makes sure the workplace is fair and respectful for as long as someone works there.
In India, the Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) HR policy ensures everyone gets a fair chance at jobs and promotions, regardless of their background. This idea is backed by India’s Constitution, especially Article 16, which says no one can be discriminated against because of their religion, race, caste, sex, or where they were born when it comes to jobs. This means companies must follow EEO rules, making sure job decisions are based on what someone can do, not who they are. EEO isn’t just for hiring; it’s a rule that makes sure the workplace is fair and respectful for as long as someone works there.
5) Anti-Discrimination Policy
 Having this policy shows that a company is committed to treating everyone equally, which is good for the company’s reputation and makes more people want to work there. It’s not just about being fair because it’s the right thing to do or because the law says so; it’s also about making sure everyone knows what behavior is okay at work. Laws such as the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace Act, 2013, the Equal Remuneration Act, 1976, and the Articles 14, 15, and 16 of the Indian Constitution all seek to prevent discrimination in the workplace and provide equality and justice for every employee.
Having this policy shows that a company is committed to treating everyone equally, which is good for the company’s reputation and makes more people want to work there. It’s not just about being fair because it’s the right thing to do or because the law says so; it’s also about making sure everyone knows what behavior is okay at work. Laws such as the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace Act, 2013, the Equal Remuneration Act, 1976, and the Articles 14, 15, and 16 of the Indian Constitution all seek to prevent discrimination in the workplace and provide equality and justice for every employee.
If there is a case where a female employee is unfairly passed over for promotions due to her gender, the Anti-Discrimination Policy offers her the deserved solution. This HR policy will make sure her complaint is investigated and that appropriate corrective action—such as a promotion she deserves and steps to prevent bias—are implemented.
6) Whistleblower Policy
 A whistleblower HR policy allows staff members to report fraud and other misconduct without facing consequences. It guarantees their safety, outlines the reporting procedure, and provides information on how to report. Though there aren’t many explicit rules for whistleblower protection in India, the Companies Act, 2013 encourages whistleblowers to prevent fraud to improve how businesses work. Such a policy is essential because it creates a culture where honesty is taken seriously and keeps the business safe.
A whistleblower HR policy allows staff members to report fraud and other misconduct without facing consequences. It guarantees their safety, outlines the reporting procedure, and provides information on how to report. Though there aren’t many explicit rules for whistleblower protection in India, the Companies Act, 2013 encourages whistleblowers to prevent fraud to improve how businesses work. Such a policy is essential because it creates a culture where honesty is taken seriously and keeps the business safe.
In 2001, Sherron Watkins, a vice president at Enron, reported accounting fraud within the company. Despite the risk to her job, she alerted Enron’s CEO about financial issues that could ruin the company. Her brave act later became crucial in revealing the Enron scandal, showing the importance of speaking up against wrongdoing and becoming a whistleblower.
7) Drug and Alcohol Policy
 The Drug and Alcohol Abuse HR Policy attempts to keep the workplace safe and productive by prohibiting the use of narcotics and/or alcohol to maintain a professional workspace that does not compromise on performance and safety. It is put to use throughout working hours and on company grounds, including company functions and business excursions. This policy is critical for preventing accidents, improving employee well-being, and maintaining efficient operations. It is especially significant under Indian legislation like the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act of 1985, which govern the usage of such substances.
The Drug and Alcohol Abuse HR Policy attempts to keep the workplace safe and productive by prohibiting the use of narcotics and/or alcohol to maintain a professional workspace that does not compromise on performance and safety. It is put to use throughout working hours and on company grounds, including company functions and business excursions. This policy is critical for preventing accidents, improving employee well-being, and maintaining efficient operations. It is especially significant under Indian legislation like the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act of 1985, which govern the usage of such substances.
This policy covers:
- Specifies conditions for drug/alcohol testing, like random checks.
- Bans illegal drugs and misuse of prescription meds.
- Outlines steps from rehabilitation support to disciplinary actions for violations.
- No use, possession, or distribution of drugs/alcohol at work.
Compensation and Benefits Policies:
8) Maternity Leave Policy
 The Maternity Leave HR policies in India follows the Maternity Benefit Act of 2017. India made significant changes to its Maternity Benefit Act, enhancing support for working mothers. Now, women are entitled to 26 weeks of paid leave for the first two children and 12 weeks for any subsequent children, provided they’ve worked at least 80 days in the past year before their due date. This move aims to bolster maternal health and child well-being, making fully sure mothers have ample time for childbirth and care without the stress of job security.
The Maternity Leave HR policies in India follows the Maternity Benefit Act of 2017. India made significant changes to its Maternity Benefit Act, enhancing support for working mothers. Now, women are entitled to 26 weeks of paid leave for the first two children and 12 weeks for any subsequent children, provided they’ve worked at least 80 days in the past year before their due date. This move aims to bolster maternal health and child well-being, making fully sure mothers have ample time for childbirth and care without the stress of job security.
Additionally, the Act mandates workplace amenities like clean restrooms and safe drinking water, and prohibits assigning strenuous tasks to pregnant employees in the weeks leading up to delivery. Employers are also encouraged to offer flexible work arrangements and wellness programs. Importantly, the Act protects women from being dismissed due to pregnancy, ensuring their right to return to work.
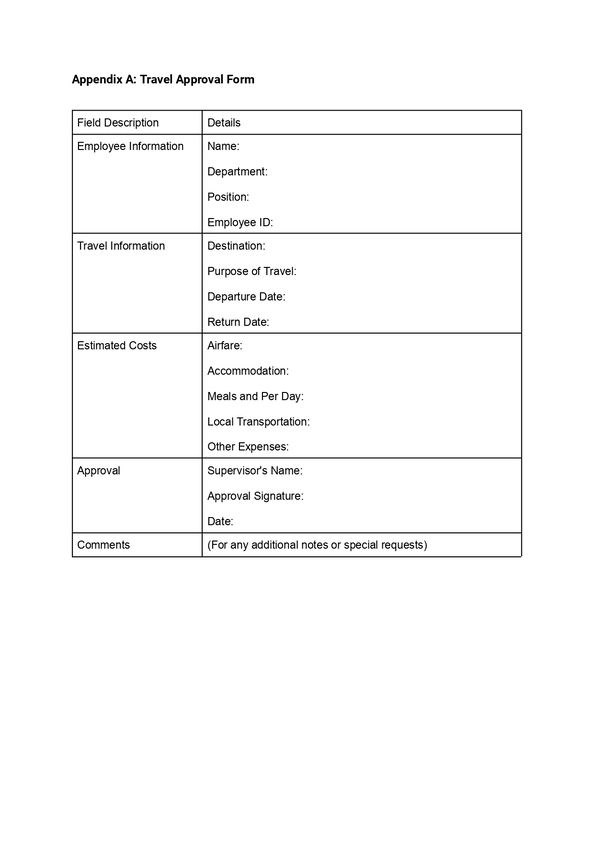
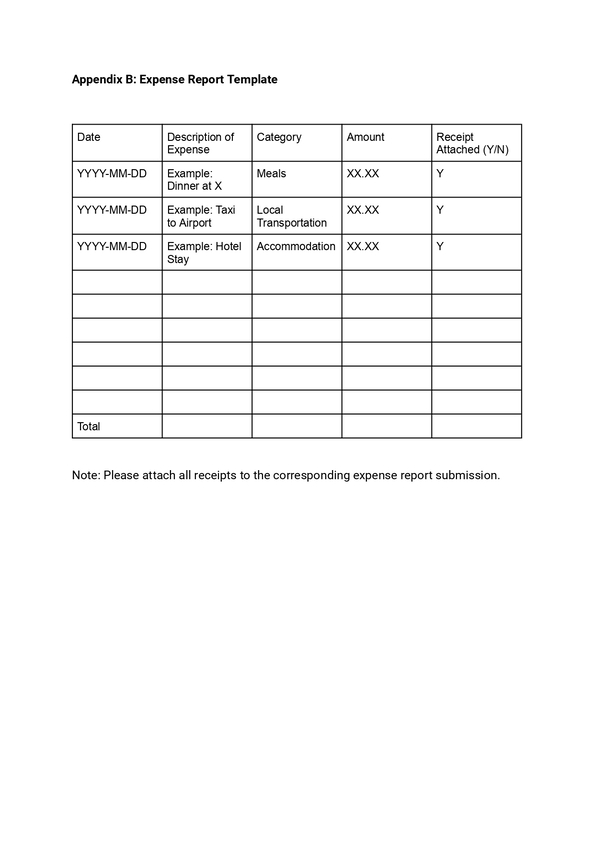
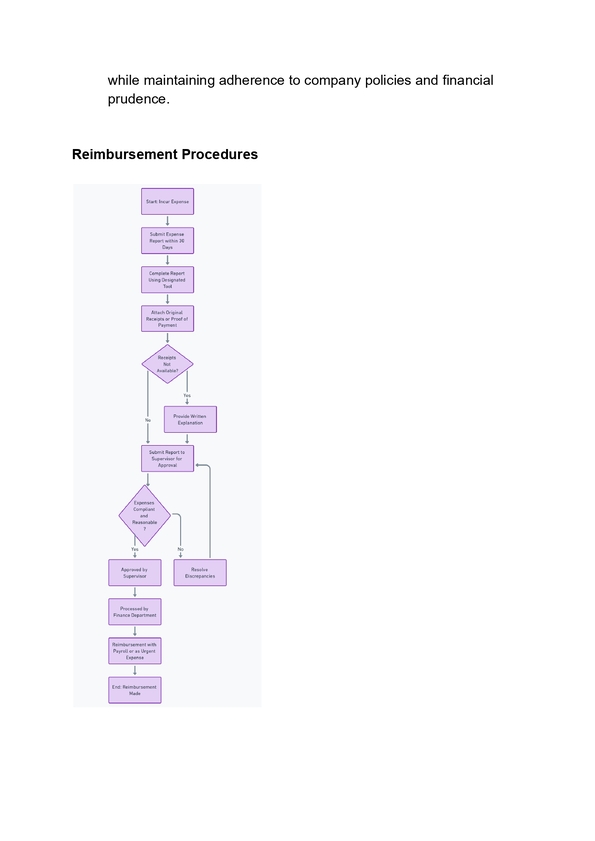
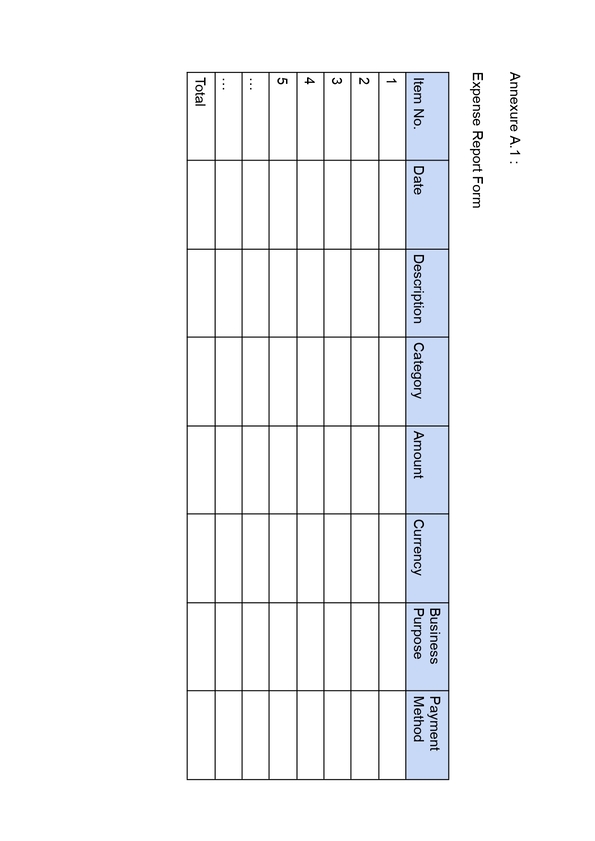
9) Expenses Reimbursement Policy
 Paying employees back for money they’ve spent on work-related expenses, such as supplies or travel, is known as expenses reimbursement. While it’s not always required, it’s standard procedure to prevent workers from covering their own expenses. Usually, the HR or finance department takes care of it. It’s important because it guarantees that employees won’t be fined financially for doing their jobs, and it benefits the business by preserving trust and employee morale.
Paying employees back for money they’ve spent on work-related expenses, such as supplies or travel, is known as expenses reimbursement. While it’s not always required, it’s standard procedure to prevent workers from covering their own expenses. Usually, the HR or finance department takes care of it. It’s important because it guarantees that employees won’t be fined financially for doing their jobs, and it benefits the business by preserving trust and employee morale.
For example, if an employee goes to a conference for work, the company will cover the costs of their hotel stay and travel, like plane tickets or gas for their car. This way, the employee doesn’t have to spend their own money to do their job.
10) Overtime Policy
 In India, laws make sure that employees who work extra hours get paid more, which is really important in busy industries. The Factories Act of 1948 says workers can’t work more than 9 hours a day or 48 hours a week. If they do, they get paid double for the extra time. Similar rules are in the Karnataka Shops and Commercial Establishment Act, 1961, which also limits how much overtime you can do – no more than fifty hours in three months. This helps ensure that workers are fairly paid for their extra effort.
In India, laws make sure that employees who work extra hours get paid more, which is really important in busy industries. The Factories Act of 1948 says workers can’t work more than 9 hours a day or 48 hours a week. If they do, they get paid double for the extra time. Similar rules are in the Karnataka Shops and Commercial Establishment Act, 1961, which also limits how much overtime you can do – no more than fifty hours in three months. This helps ensure that workers are fairly paid for their extra effort.
11) Sales Commission Policy
A Sales Commission Policy clearly outlines how sales teams are compensated, factoring in their performance and sales achievements. Employees responsible for commission payments must balance their budget for commissions with varying sales levels, base salaries, and potential bonuses. Fair commission rates can differ by industry and role, influenced by product value, the sales effort, and territory size.
Commission calculations often use fixed percentages, tiered rewards for higher sales, or bonuses for exceeding targets. Tools like CRM software help in accurately tracking sales and ensuring commissions are fairly calculated, aligning with the policy’s guidelines.For an in-depth look at crafting an effective Sales Commission Policy, visit our blog on sales commission.
12) Employee Provident Fund Policy
 The EPF and EPS policy is important because it helps employees save money for when they retire, giving them peace of mind about their future. It also makes employees feel safe, knowing they and their families will be taken care of later on. The Employee Provident Fund (EPF) and Employee Pension Scheme (EPS) are designed for salaried employees under the 1952 Employees’ Provident Funds Act.
The EPF and EPS policy is important because it helps employees save money for when they retire, giving them peace of mind about their future. It also makes employees feel safe, knowing they and their families will be taken care of later on. The Employee Provident Fund (EPF) and Employee Pension Scheme (EPS) are designed for salaried employees under the 1952 Employees’ Provident Funds Act.
Both employees and employers contribute 12% of the basic salary to the fund, totaling a 24% contribution each month. Of the employer’s portion, 3.67% is allocated to the EPF, with the remaining 8.33% going to EPS. The EPF interest rate is set at 8.8% annually. Employees can nominate their parents, spouse, or children as beneficiaries for EPF benefits. Contributions to the EPF are tax-deductible under section 80C of the Income Tax Act.
13) Employee Wages Policy
 Handling employee wages means making sure paychecks are right and fair, and follow the law. The Minimum Wages Act, 1948, tells us the least amount workers should get, enough to live on. HR can use special software to make figuring out pay easier, making sure everything’s correct and legal. They also check things regularly and keep up with any new rules.
Handling employee wages means making sure paychecks are right and fair, and follow the law. The Minimum Wages Act, 1948, tells us the least amount workers should get, enough to live on. HR can use special software to make figuring out pay easier, making sure everything’s correct and legal. They also check things regularly and keep up with any new rules.
An ideal wage calculation would look like so:
- Hourly Rates: You will need to multiply hours worked by the hourly rate. Overtime is usually paid at 1.5 times the regular rate.
- Salaries: It is a fixed amount per pay period, detailed in the employment contract, divided by annual pay periods.
14) Compensation and Benefits Policy
 The Compensation and Benefits HR Policy establishes how and how much employees are paid, as well as what additional benefits they will receive. These HR policies in India increases employee work satisfaction and loyalty. It is critical to attract top talent and retain competent personnel by providing competitive packages that go beyond salary. This strategy is actively implemented throughout yearly evaluations, promotions, and updates to business benefits in response to market developments or employee feedback.
The Compensation and Benefits HR Policy establishes how and how much employees are paid, as well as what additional benefits they will receive. These HR policies in India increases employee work satisfaction and loyalty. It is critical to attract top talent and retain competent personnel by providing competitive packages that go beyond salary. This strategy is actively implemented throughout yearly evaluations, promotions, and updates to business benefits in response to market developments or employee feedback.
According to a survey by Willis Towers Watson, their “2020 India Benefits Trends Survey” found that 53% of Indian companies are enhancing or planning to enhance their health and wellness benefits to retain and attract talent. Such an approach is significant in India because it helps enterprises comply with legislation such as the Minimum Wage Act and the Provident Funds Act, so that everyone receives a fair deal.
15) Gratuity Policy
 The Gratuity HR Policy in India is a form of appreciation for employees’ dedicated service, as mandated by the Payment of Gratuity Act of 1972. This law requires companies with ten or more employees to provide a gratuity after a minimum of five years of service. The gratuity amount is determined by the employee’s last drew paycheck, which includes basic pay and dearness allowance, as well as the number of years of service. Gratuity is calculated using the formula (15 × final wage × service years)/26, which guarantees a fair evaluation based on tenure and earnings.
The Gratuity HR Policy in India is a form of appreciation for employees’ dedicated service, as mandated by the Payment of Gratuity Act of 1972. This law requires companies with ten or more employees to provide a gratuity after a minimum of five years of service. The gratuity amount is determined by the employee’s last drew paycheck, which includes basic pay and dearness allowance, as well as the number of years of service. Gratuity is calculated using the formula (15 × final wage × service years)/26, which guarantees a fair evaluation based on tenure and earnings.
By including gratuity into the Cost to Company (CTC), companies can openly track this benefit, which is also covered by income tax rules, and match it with the larger framework of employee remuneration.
16) Grievance Handling Policy
 The Grievance Handling HR policies in India are intended to address and resolve employee complaints such as unjust treatment, workplace harassment, and salary issues. This rule establishes a formal process for employees to express their concerns, so that they are heard and addressed properly, which is critical for preserving a positive work environment. It applies to all employees, regardless of position, and should be used when dealing with issues at work. It kicks in when an employee raises an issue covered by the policy. This strategy is extremely important for retaining talented employees since it immediately solves their concerns, prevents matters from becoming worse, and builds a caring work environment.
The Grievance Handling HR policies in India are intended to address and resolve employee complaints such as unjust treatment, workplace harassment, and salary issues. This rule establishes a formal process for employees to express their concerns, so that they are heard and addressed properly, which is critical for preserving a positive work environment. It applies to all employees, regardless of position, and should be used when dealing with issues at work. It kicks in when an employee raises an issue covered by the policy. This strategy is extremely important for retaining talented employees since it immediately solves their concerns, prevents matters from becoming worse, and builds a caring work environment.
The Grievance Handling HR Policy includes:
- How It Works: Explains the steps to handle a complaint.
- What Counts: Defines what a grievance is.
- When to Report: Tells when you need to report an issue.
- Steps to Solve: Lists how to move from complaint to solution.
- Who to Talk To: Shows who you can go to with your problem.
- What If Not Solved: Guides on what to do if the issue isn’t fixed.
- How to Appeal: Provides ways to challenge the final decision.
Workplace Safety and Health Policies:
17) Health and Safety Policy
 For the purpose of guaranteeing a safe and healthy workplace, India’s Health and Safety HR Policy is very important. Laws such as the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code of 2020 and the Factories Act of 1948 serve as this HR policy’s guidelines. It is vital in all businesses, but it is particularly important in the manufacturing, construction, and chemical sectors because these industries need steps to safeguard workers from any kind of occupational dangers. It requires emergency response training, frequent drills, and safety procedures. The Bhopal Gas Disaster of 1984 serves as an important reminder of the serious need for strict health and safety regulations in companies handling potentially hazardous substances. This incident resulted in higher regulatory supervision and increased health and safety protocols across Indian industry.
For the purpose of guaranteeing a safe and healthy workplace, India’s Health and Safety HR Policy is very important. Laws such as the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code of 2020 and the Factories Act of 1948 serve as this HR policy’s guidelines. It is vital in all businesses, but it is particularly important in the manufacturing, construction, and chemical sectors because these industries need steps to safeguard workers from any kind of occupational dangers. It requires emergency response training, frequent drills, and safety procedures. The Bhopal Gas Disaster of 1984 serves as an important reminder of the serious need for strict health and safety regulations in companies handling potentially hazardous substances. This incident resulted in higher regulatory supervision and increased health and safety protocols across Indian industry.
18) Workplace Violence Prevention Policy
 Any type of violence at work lowers work quality and can hurt the company’s image. An HR aims to keep the workplace safe and solve problems peacefully. Hence, workplace violence HR Policy ensures a safe and respected workplace by strictly prohibiting all forms of violence and conflict. It exists to protect employee well-being and security, stressing that violence is not a proper means of conflict resolution. This rule applies to all company members, regardless of their position, and takes effect at any sign of violence, whether verbal, physical, or psychological.
Any type of violence at work lowers work quality and can hurt the company’s image. An HR aims to keep the workplace safe and solve problems peacefully. Hence, workplace violence HR Policy ensures a safe and respected workplace by strictly prohibiting all forms of violence and conflict. It exists to protect employee well-being and security, stressing that violence is not a proper means of conflict resolution. This rule applies to all company members, regardless of their position, and takes effect at any sign of violence, whether verbal, physical, or psychological.
19) Hybrid Work Model Policy
 The Hybrid Work Model in India combines office and remote work, offering employees the flexibility to choose their work location based on job requirements and personal preferences. Some types of hybrid work models are:
The Hybrid Work Model in India combines office and remote work, offering employees the flexibility to choose their work location based on job requirements and personal preferences. Some types of hybrid work models are:
- Flexible Hybrid: Employees choose their in-office and remote days
- Fixed Hybrid: Set days for in-office and remote work
- Office-First Hybrid: Primarily office-based with occasional remote work
- Remote-First Hybrid: Mainly remote with occasional office visits.
Today’s Hybrid Work Model HR policy should include guidelines on work location and schedules, specifying who can work remotely and how often. It should have a system for booking office resources like desks and meeting rooms. Clear communication rules, technology support for remote work, and adherence to health and safety standards are essential.
Employee Conduct Policies
20) Anti Bullying Policy
 Bullying at the workplace can manifest as spreading harmful rumors, unfair treatment, singling out or undermining someone, and blocking professional opportunities like training or promotions. Although India doesn’t have a specific anti-bullying law, such actions can be tackled under the Indian Penal Code (IPC). Sections like 339 for wrongful restraint, 340 for wrongful confinement, 506 for criminal intimidation, 323 for causing hurt, and 306 for abetment of suicide provide legal recourse. These laws help tackle the seriousness of workplace bullying, offering victims a pathway to seek justice and making sure that workplaces strive to be environments of respect and safety, free from harassment.
Bullying at the workplace can manifest as spreading harmful rumors, unfair treatment, singling out or undermining someone, and blocking professional opportunities like training or promotions. Although India doesn’t have a specific anti-bullying law, such actions can be tackled under the Indian Penal Code (IPC). Sections like 339 for wrongful restraint, 340 for wrongful confinement, 506 for criminal intimidation, 323 for causing hurt, and 306 for abetment of suicide provide legal recourse. These laws help tackle the seriousness of workplace bullying, offering victims a pathway to seek justice and making sure that workplaces strive to be environments of respect and safety, free from harassment.
21) Attendance And Punctuality Guidelines
 An Attendance and Punctuality HR Policy typically covers rules like work hours, how to report absences or lateness, procedures for requesting time off, and consequences for unexcused absences or habitual tardiness. For example, this policy can be used when an employee consistently arrives late, impacting team productivity. The policy would guide the manager on how to document the behavior, discuss it with the employee, and apply any necessary disciplinary actions according to the outlined procedures.
An Attendance and Punctuality HR Policy typically covers rules like work hours, how to report absences or lateness, procedures for requesting time off, and consequences for unexcused absences or habitual tardiness. For example, this policy can be used when an employee consistently arrives late, impacting team productivity. The policy would guide the manager on how to document the behavior, discuss it with the employee, and apply any necessary disciplinary actions according to the outlined procedures.
According to a report by the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), businesses can lose up to 4% of their annual revenue due to absenteeism and tardiness, highlighting the importance of a solid Attendance and Punctuality HR P
22) Dress Code Policy
 In India, establishing a dress code guideline contributes to the upkeep of a formal environment at work. The company’s definition of formal, informal, and business casual clothes is spelt out in detail, which facilitates understanding among employees of all genders and positions. For example, in order to maintain a formal environment, State Bank of India‘s 2019 dress code policy discouraged the wearing of jeans and T-shirts.
In India, establishing a dress code guideline contributes to the upkeep of a formal environment at work. The company’s definition of formal, informal, and business casual clothes is spelt out in detail, which facilitates understanding among employees of all genders and positions. For example, in order to maintain a formal environment, State Bank of India‘s 2019 dress code policy discouraged the wearing of jeans and T-shirts.
In a typical Indian workplace dress code policy, you might find some of these following guidelines:
Allowed:
- Formal Indian Wear: Sarees or salwar kameez for women, formal shirts and trousers for men, commonly seen in banks and government offices.
- Business Casual: Kurtas, smart casual shirts, and trousers, preferred in IT firms like Infosys.
- Western Formal: Suits for men, pantsuits for women, typical in multinational companies.
Not Allowed:
- Casual Wear: Shorts, flip-flops, and tank tops are usually not acceptable.
- Revealing Outfits: Overly revealing clothes are discouraged to keep a professional look.
- Bright Colors/Loud Prints: Very bright colors and bold prints might be seen as distracting in traditional sectors.
23) Employee Gift Policy
 It’s important to have clear rules about gifts at work. This helps keep things fair and honest. The rules say who can give or get gifts and when. This stops any problems or wrong ideas about why someone gave a gift. People in big jobs with lots of power have stricter rules. This is to make sure everything stays fair. Sometimes, small gifts for festivals or traditions are okay. This respects India’s rich culture and celebrations.
It’s important to have clear rules about gifts at work. This helps keep things fair and honest. The rules say who can give or get gifts and when. This stops any problems or wrong ideas about why someone gave a gift. People in big jobs with lots of power have stricter rules. This is to make sure everything stays fair. Sometimes, small gifts for festivals or traditions are okay. This respects India’s rich culture and celebrations.
There are some companies that have their own guidelines on gifts. For example- Adobe values innovation and creativity in their gift policy. The company’s basic ideals and dedication to supporting a creative work environment are reflected in the policy, which encourages the exchange of presents that stimulate creativity, such as books, art supplies, or software tools.
24) Code of Conduct
 This HR policy is similar to a set of guidelines for how employees should conduct themselves as a professional. It implies that everyone treats one another fairly and lives by the company’s policies by stating what is and is not acceptable at work. It matches other rules that promote companies to act properly and maintain a positive workplace culture. This means telling everyone about these guidelines, making that everyone is aware of them, and applying them equally to everyone, according to HR managers. In order to maintain a polite and respectful work environment for everybody, HR must intervene when someone disobeys the rules, investigate the situation, and make the necessary corrections.
This HR policy is similar to a set of guidelines for how employees should conduct themselves as a professional. It implies that everyone treats one another fairly and lives by the company’s policies by stating what is and is not acceptable at work. It matches other rules that promote companies to act properly and maintain a positive workplace culture. This means telling everyone about these guidelines, making that everyone is aware of them, and applying them equally to everyone, according to HR managers. In order to maintain a polite and respectful work environment for everybody, HR must intervene when someone disobeys the rules, investigate the situation, and make the necessary corrections.
25) Social Media Policy
 The Social Media HR Policy tells employees the right way to use sites like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. It sets rules on what they can and can’t post to make sure they and the company look good online. Strict guidelines under the Social Media HR Policy include:
The Social Media HR Policy tells employees the right way to use sites like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. It sets rules on what they can and can’t post to make sure they and the company look good online. Strict guidelines under the Social Media HR Policy include:
Brand Representation: Constantly convey the tone and values of the company as a whole.
Maintaining confidentiality: Avoid disclosing private or confidential firm information.
Professionalism: Always conduct yourself in a professional manner in all posts and communications.
Account Management: Only authorized employees can see and update corporate accounts.
Legal Compliance: Comply with copyright regulations and add any required disclosures.
Personal Accounts: Avoid posting anything that would reflect adversely on the company on your personal accounts; instead, keep them private or professional.
26) Menstrual Leave Policy
 An increasing number of Indian women and menstruating individuals are taking advantage of the Menstrual Leave HR Policy, which allows them to take several days off work, usually with compensation, to help with their period discomfort. Understanding that menstruation can have a substantial influence on a woman’s everyday life and productivity at work, this policy seeks to help women’s health and well-being.
An increasing number of Indian women and menstruating individuals are taking advantage of the Menstrual Leave HR Policy, which allows them to take several days off work, usually with compensation, to help with their period discomfort. Understanding that menstruation can have a substantial influence on a woman’s everyday life and productivity at work, this policy seeks to help women’s health and well-being.
In India, menstrual leave has recently gained significant attention following a dispute triggered by a statement made by a well-known figure. Though not yet popular nationwide, a few forward-thinking businesses and governments have started to implement this policy, which provides up to three days of menstruation leave per month. Businesses that have implemented menstrual leave, such as Zomato and Culture Machine, got media attention and served as role models for other companies.
Data and Information Security Policies:
27) Company Data Protection Policy
 For any business, this policy is critical given that it means that everyone understands how to handle sensitive information responsibly. These particular HR policies in India :
For any business, this policy is critical given that it means that everyone understands how to handle sensitive information responsibly. These particular HR policies in India :
- Respects fundamental guidelines for appropriately and fairly managing personal information
- Identifies the person responsible for ensuring the security of firm information
- Checks and updates the policy on a regular basis to reflect new regulations and technology
- Outlines procedures for protecting data and what steps to take incase it is disclosed.
- Monitors the use of information to show appropriate handling
In India, a new law called the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 has been introduced. This important law starts a new way of protecting a company’s data in the digital world. It aims to give people more control over their personal information, change how businesses handle data, and make sure data is used responsibly and how companies collect and use personal data.
28) Record Maintenance And Confidentiality Policy
 A Record Maintenance and Confidentiality HR Policies in India is a set of guidelines within an organization that outlines how employee records, company data, and sensitive information should be handled, stored, and protected.
A Record Maintenance and Confidentiality HR Policies in India is a set of guidelines within an organization that outlines how employee records, company data, and sensitive information should be handled, stored, and protected.
HR professionals should keep in mind that documents related to employee contracts, personal information, performance reviews, disciplinary actions, and training logs are important for maintaining confidentiality and maintaining records. In addition, non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), access control logs, and data protection policies all help keep confidentiality and guarantee that private information is handled safely and in compliance with privacy regulations.
For example, IBM‘s 2020 report on data breaches found that, on average, a data breach could cost a company about $3.86 million. This shows how important it is for companies to have strong rules to protect their data.
29) Internet And Email Policy For Employees
 A Computer or Internet Usage and Email Policy sets the rules for how employees can use company technology and email. It’s there to stop any misuse that could harm the company’s legal standing or reputation.
A Computer or Internet Usage and Email Policy sets the rules for how employees can use company technology and email. It’s there to stop any misuse that could harm the company’s legal standing or reputation.
Strict guidelines in this HR policies in India often include the following: no downloading unauthorized software to avoid malware risks; no visiting non-work-related websites, particularly those that are unsafe or inappropriate; and guidelines on sending personal emails so as not to interfere with work obligations or compromise company data. The policy helps promote the setting up of a secure and professional digital work environment by outlining these limits.
30) Laptop Policy
 To guarantee that computers provided by the company are being used properly, an employee laptop policy has been developed. HR departments and managers frequently work with IT teams to develop this HR policies in India. Device management software is one example of a tool that facilitates remote monitoring, data security, and policy compliance enforcement.
To guarantee that computers provided by the company are being used properly, an employee laptop policy has been developed. HR departments and managers frequently work with IT teams to develop this HR policies in India. Device management software is one example of a tool that facilitates remote monitoring, data security, and policy compliance enforcement.
In many companies, only employees who need to work on the go, like those in sales or IT, get company laptops. These laptops should mainly be used for work to keep things secure and make sure everyone stays productive. To keep the laptops safe, employees need to follow certain rules, like using strong passwords, keeping data encrypted, and not letting others use their work laptop. If there are any issues or damage to the laptop, it’s important to tell the IT department right away so they can fix it. Also, when an employee leaves the company, they need to give the laptop back in good shape, except for the usual wear and tear from using it.
31) Employee Privacy Policy
 Companies create an Employee Privacy Policy to keep workers’ personal info safe. This policy explains what kind of personal details the company keeps, like job records, and how they protect this info from getting out. Only certain people in the company can see this data, and there are strict rules on how to handle and store it safely. The policy also tells employees what to do if there’s a data leak. Companies use special software to help keep data safe and train employees on how to keep information private. This helps everyone trust that their personal details are well-protected at work.
Companies create an Employee Privacy Policy to keep workers’ personal info safe. This policy explains what kind of personal details the company keeps, like job records, and how they protect this info from getting out. Only certain people in the company can see this data, and there are strict rules on how to handle and store it safely. The policy also tells employees what to do if there’s a data leak. Companies use special software to help keep data safe and train employees on how to keep information private. This helps everyone trust that their personal details are well-protected at work.
32) Anti-Spam Policy
 Businesses create anti-spam human resources rules to guarantee that emails, particularly those used for marketing, are polite and compliant. Anti-Spam HR policies in India include things like getting permission from the recipient before sending emails, making sure the content is professional and relevant, clearly identifying the sender, and offering a simple unsubscribe option. These standards, which are intended to abide by the Information Technology Act of 2000, call for the use of email management technologies to monitor obedience, policy training for staff members, as well as regular audits to guarantee continued compliance.
Businesses create anti-spam human resources rules to guarantee that emails, particularly those used for marketing, are polite and compliant. Anti-Spam HR policies in India include things like getting permission from the recipient before sending emails, making sure the content is professional and relevant, clearly identifying the sender, and offering a simple unsubscribe option. These standards, which are intended to abide by the Information Technology Act of 2000, call for the use of email management technologies to monitor obedience, policy training for staff members, as well as regular audits to guarantee continued compliance.
Recruitment and Termination Policies:
33) Employee Referral Program Policy
 An Employee Referral Program Policy helps employees to suggest people they know for jobs at their company. Th HR policies in India explain things like referral bonuses, which are special rewards for recommending someone who gets hired. Some jobs might offer bigger rewards if they’re hard to fill. The policy says who can suggest candidates (usually not HR or top bosses) and how much the rewards are. For instance, a regular referral could earn someone Rs. 10,000, but a harder-to-fill tech job might get Rs. 20,000. The policy also makes sure everything follows tax laws, so everyone knows how bonuses will be handled tax-wise.
An Employee Referral Program Policy helps employees to suggest people they know for jobs at their company. Th HR policies in India explain things like referral bonuses, which are special rewards for recommending someone who gets hired. Some jobs might offer bigger rewards if they’re hard to fill. The policy says who can suggest candidates (usually not HR or top bosses) and how much the rewards are. For instance, a regular referral could earn someone Rs. 10,000, but a harder-to-fill tech job might get Rs. 20,000. The policy also makes sure everything follows tax laws, so everyone knows how bonuses will be handled tax-wise.
34) Exit Interview Policy
 Even the most satisfied employees will eventually leave your company due to resignation, redundancy, or retirement. Having an exit policy in place is crucial to manage the steps and actions needed when an employee decides to leave or is let go.
Even the most satisfied employees will eventually leave your company due to resignation, redundancy, or retirement. Having an exit policy in place is crucial to manage the steps and actions needed when an employee decides to leave or is let go.
The questions asked are straightforward, aiming to get helpful feedback without making the employee uncomfortable. It also includes steps to look into any reports of poor behavior by colleagues that might have pushed the employee to leave. Tools like questionnaires and feedback forms are often used, and the process is designed to be respectful and confidential, helping the company learn and improve from each departure.
Here is list of some example questions asked in this exit interview:
- What made you decide to begin your new job search?
- Did you feel prepared to perform this task well?
- What would you say about our company’s culture?
- Have you had enough feedback on your performance?
- What aspects of your job were your favorite?
- What part of your working environment could have been improved?
- What are your thoughts on this place’s leadership and management?
- Were there any rules or guidelines that you found challenging to follow?
- Could you offer any recommendations on how we could get better?
- What factors of working here will you miss the most?
34) Recruitment and Hiring Policy
 For impartial and consistent recruiting procedures and to draw in top talent for the growth of the company, an HR manager must definitely have a Recruitment and Hiring HR Policies in India. Selection criteria, interviews, job listings, application procedures, and onboarding processes are only a few of the topics covered by such recruitment policies. Clarity and equality in special cases, such as internal transfers or referrals, are covered under the rules and exceptions of this policy. It can be a useful tool when filling a newly formed position, replacing a leaving employee, or growing the team.
For impartial and consistent recruiting procedures and to draw in top talent for the growth of the company, an HR manager must definitely have a Recruitment and Hiring HR Policies in India. Selection criteria, interviews, job listings, application procedures, and onboarding processes are only a few of the topics covered by such recruitment policies. Clarity and equality in special cases, such as internal transfers or referrals, are covered under the rules and exceptions of this policy. It can be a useful tool when filling a newly formed position, replacing a leaving employee, or growing the team.
36) Termination and Separation Policy
 In a workplace, the terms “termination” and “separation” relate to the process of terminating an employee’s job or contract with the company. In order to handle this, an HR manager has to
In a workplace, the terms “termination” and “separation” relate to the process of terminating an employee’s job or contract with the company. In order to handle this, an HR manager has to
-stick to company and legal standards
-make sure the process is fair, polite, and documented
-give clear support and communication to the departing employee and remaining team members.
It outlines the reasons for termination, necessary notifications, and departure procedures. When Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) carried out a restructuring process in 2014–2015, which resulted in the firing of several employees, this policy was put into action. The corporation took a disciplined approach to managing personnel changes by offering severance compensation and adhering to internal HR regulations and legal requirements. The team also maintained transparent communication.
37) Probation and Confirmation Policy
The Probation and Confirmation HR Policy gives new hires a trial term to assess their performance and cultural fit with the company. It details the trial’s duration, performance evaluation criteria, and feedback provided. Employees receive approval for permanent roles only if they satisfy the requirements. Next the employers are required by the Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1946 to specify the terms of employment, and this policy complies with the more general principles of fair employment practices.
The HR Policy for Probation and Confirmation includes the following:
- Trial Period Duration: Indicates how long the probation term will last.
- Performance Evaluation Criteria: Specifies the conditions that are used to evaluate an employee’s work.
- Frequent Feedback: Makes sure that expectations and performance are continuously communicated.
- Training and Support: Offers tools to help new hires be successful.
- Confirmation Criteria: Breaks down the necessary steps for getting permanent status.
- Extension Terms: Lists the circumstances in which the period of probation may be extended.
- Termination Guidelines: Describes situations in which a probationary employee could be let go.
- Confirmation Process: Outlines the procedures to verify a worker’s long-term position.
38) Employee Onboarding and Offboarding Policy
 The Employee Onboarding and Offboarding HR policies in India outlines the detailed steps for welcoming new employees into the company and smoothly transitioning out those who are leaving. Both scenarios place your company at significant risk, even if just one small step is missed in the process. Let’s look at some of the steps under this policy an HR needs to follow for a successful onboarding and offboarding process:
The Employee Onboarding and Offboarding HR policies in India outlines the detailed steps for welcoming new employees into the company and smoothly transitioning out those who are leaving. Both scenarios place your company at significant risk, even if just one small step is missed in the process. Let’s look at some of the steps under this policy an HR needs to follow for a successful onboarding and offboarding process:
Onboarding Steps:
- Pre-arrival communication.
- First-day orientation.
- Role and responsibilities briefing.
- Introduction to team and mentor.
- Training and development programs.
- Access to tools and systems.
- Regular check-ins and feedback.
Offboarding Steps:
- Notice of termination/resignation.
- Exit interview.
- Final settlement processing.
- Company assets return.
- System access revocation.
- Handover of duties.
- Farewell and acknowledgement.
39) Employment Contracts/Agreement
 To encourage openness and understanding, employee contracts and agreements explain job responsibilities, pay, perks, working hours, and termination policies. These HR policies in India makes sure that all employment conditions are valid by complying with Indian regulations such as the Indian Contract Act, 1872, and provides employers and employees with clear expectations and legal bounds.
To encourage openness and understanding, employee contracts and agreements explain job responsibilities, pay, perks, working hours, and termination policies. These HR policies in India makes sure that all employment conditions are valid by complying with Indian regulations such as the Indian Contract Act, 1872, and provides employers and employees with clear expectations and legal bounds.
Under these HR policies in India, a few crucial contracts and agreements include:
- Performance Review Agreement
- Arbitration Agreement
- Data Protection Agreement
- Intellectual Property Agreement
- Relocation Agreement
- Training and Development Agreement
- Flexible Working Hours Agreement
- Severance Agreement
- Equal Opportunity Employment Agreement
- Health and Safety Agreement
- Grievance Handling Procedure Agreement
- Remote Work Equipment Agreement
- Expense Reimbursement Agreement
40) Non-Compete and Non-Solicitation Policy
 A non-solicitation agreement prevents an individual from poaching clients or employees from their former employer, safeguarding the company’s internal and client relationships. Conversely, a non-compete agreement restricts the individual from initiating or joining a competing business, thus protecting the company’s proprietary information and competitive standing in the market.
A non-solicitation agreement prevents an individual from poaching clients or employees from their former employer, safeguarding the company’s internal and client relationships. Conversely, a non-compete agreement restricts the individual from initiating or joining a competing business, thus protecting the company’s proprietary information and competitive standing in the market.
For HR managers to reduce risks and to safeguard the company’s work and client information, this policy is essential. Imagine a senior marketing professional at an IT company can opt to join a competitor or an employee engages with a potential client or partner company. In which case a non-compete and non-solicitation agreement comes into play.
Work-Life Balance Policies:
41) Leave and Attendance Policy
To keep discipline and order in an organization, a strong attendance policy is necessary. It makes sure staff members are aware of the risks of low attendance by describing in detail the policies on tardiness, early leaves, and unexplained absences. The following are the typical attendance standards in use:
- Advance Notice for Absences System: Employees have to give management timely advance notice of any changes to their shifts or absences in order to keep up work running smoothly.
- Point-based System: This is a responsible attendance system where employees are assigned points for absences. Once a limit is set, an HR manager can choose the appropriate disciplinary measure.
- No-Call/No-Show System: It is an attendance system that sets harsh penalties for employees who vanish without warning, which could include being fired, pointing out the importance of basic professional communication.
- Rolling Period System: This provides an opportunity for a fresh start by tracking attendance violations over a predetermined period of time, typically six to twelve months.
- Late Arrival System: It establishes the standards for tardiness and the corresponding sanctions to guarantee punctual attendance.
42) Remote Work Policy
 The HR Policies in India for Remote Work is being adopted by more and more firms in 2024 and is gaining popularity in India. It has the potential to set new guidelines for how Indians function in a workplace. Once an agreement for remote work arrangements has been established between the employer and the employee, this policy allows workers to work from home or from any other location of their choice- outside of the typical office. Because work from home (WFH) reduces the need for actual office space and resources, it can drastically lower running costs for businesses. It also makes a larger talent pool accessible, free from any geographic limitations. All things considered, HR managers in India will find this HR policy to be of great help in managing a remote workforce, making sure employees stay motivated and productive while also collecting business rewards.
The HR Policies in India for Remote Work is being adopted by more and more firms in 2024 and is gaining popularity in India. It has the potential to set new guidelines for how Indians function in a workplace. Once an agreement for remote work arrangements has been established between the employer and the employee, this policy allows workers to work from home or from any other location of their choice- outside of the typical office. Because work from home (WFH) reduces the need for actual office space and resources, it can drastically lower running costs for businesses. It also makes a larger talent pool accessible, free from any geographic limitations. All things considered, HR managers in India will find this HR policy to be of great help in managing a remote workforce, making sure employees stay motivated and productive while also collecting business rewards.
43) Menstrual Leave Policy
An increasing number of Indian women and menstruating individuals are taking advantage of the Menstrual Leave HR Policies in India, which allows them to take several days off work, usually with compensation, to help with their period discomfort. Understanding that menstruation can have a substantial influence on a woman’s everyday life and productivity at work, this policy seeks to help women’s health and well-being. In India, menstrual leave has recently gained significant attention following a dispute triggered by a statement made by a well-known figure. Though not yet popular nationwide, a few forward-thinking businesses and governments have started to implement this policy, which provides up to three days of menstruation leave per month. Businesses that have implemented menstrual leave, such as Zomato and Culture Machine, got media attention and served as role models for other companies.
44) Employee Development and Training Policy
 The Employee Development and Training Policy is key because it makes sure employees are skilled and knowledgeable enough to do their jobs well and keep up with changes in their industry. This policy helps employees grow, makes them happier at work, and boosts the company’s performance. How often training happens can actually differ and depend on how quickly things change in your particular industry, new tech or methods being introduced, and the career goals of each of your employees. While some companies might have training once a year, others might do it more often if needed or if certain rules require it. Here are some steps you need to follow as an HR manager to have a successful employee training process:
The Employee Development and Training Policy is key because it makes sure employees are skilled and knowledgeable enough to do their jobs well and keep up with changes in their industry. This policy helps employees grow, makes them happier at work, and boosts the company’s performance. How often training happens can actually differ and depend on how quickly things change in your particular industry, new tech or methods being introduced, and the career goals of each of your employees. While some companies might have training once a year, others might do it more often if needed or if certain rules require it. Here are some steps you need to follow as an HR manager to have a successful employee training process:
- Find the Gaps: Look at where employees need more skills.
- Make a Plan: Decide what you want the training to achieve.
- Get Ready: Put together the right training for those goals.
- Figure Out the Budget: Work out how much you can spend on it.
- Choose the Team: Pick which employees will join the training.
- Begin Training: Start the training sessions.
- Be There to Help: Give support to employees while they’re learning.
- See How It Went: Check if the training made a difference.
- Use It at Work: Help employees use their new skills on the job.
- Document It: Keep track of what training happened and how it can be improved.
45) Employee Recognition Policy
 An Employee Recognition Policy is about saying how you like an employee’s work and making them feel valued and more connected to the company’s goals. It’s important because it makes employees happier and more engaged. A Gallup study shows it can make teams 14% more productive. These HR policies in India includes who can get recognized, different ways to say thanks, how to pick who gets recognized, and how often to give out awards. To do this, you set clear rules, pick various rewards, and keep the process open and fair. Here are some types of employee recognitions for your employees:
An Employee Recognition Policy is about saying how you like an employee’s work and making them feel valued and more connected to the company’s goals. It’s important because it makes employees happier and more engaged. A Gallup study shows it can make teams 14% more productive. These HR policies in India includes who can get recognized, different ways to say thanks, how to pick who gets recognized, and how often to give out awards. To do this, you set clear rules, pick various rewards, and keep the process open and fair. Here are some types of employee recognitions for your employees:
- Celebration Events: Parties for team successes.
- Innovation Incentives: Rewards for creative ideas.
- Monetary Rewards: Bonuses or gift cards.
- Non-Monetary Gifts: Extra days off or company swag.
- Peer Recognition: Employees appreciating each other.
- Performance Awards: ‘Employee of the Month’ awards.
- Personal Praise: Thank-you notes or verbal thanks.
- Professional Growth: Training or advancement chances.
- Public Recognition: Highlighting efforts in meetings or announcements.
- Service Milestones: Gifts for years of service.
Sample HR Policies
Designed to structure your organisation for growth & enhance operational efficiency,Implementing these clear, concise guidelines will solidify your company’s foundation & build a safe workplace culture.
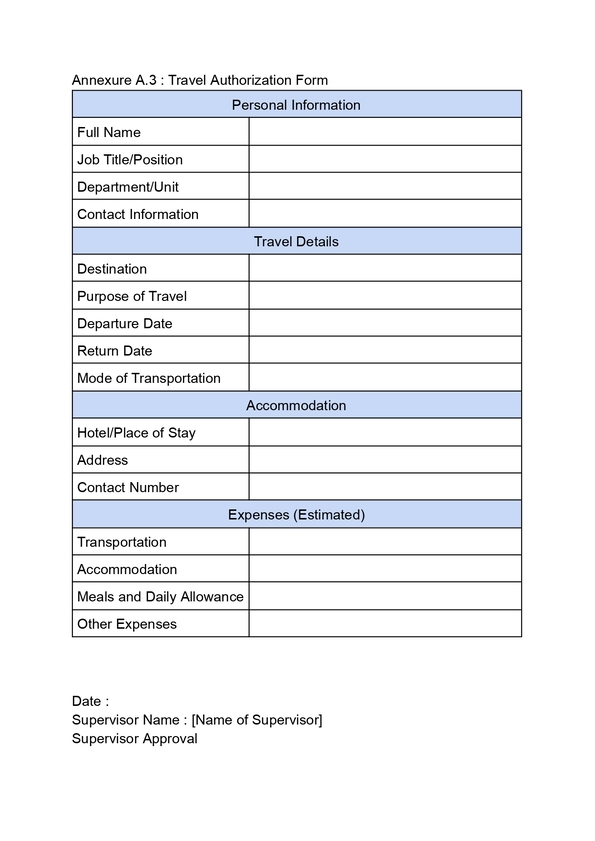
Travel Policy
Reimbursement Policy
Leave Policy
FAQ’s
1)Where can I find my company's HR policies?
Company HR policies are usually accessible on the company intranet, HR department, or employee handbook.
2)What happens if I violate an HR policy?
Violating an HR policy can lead to disciplinary action, ranging from warnings to termination, depending on the policy and severity of the violation.
3)Can HR policies differ between departments?
While core HR policies apply company-wide, some department-specific policies may vary due to different operational needs.
4)How are HR policies communicated to employees?
HR policies are communicated through orientation sessions, company intranet, emails, and regular training updates.
5)How do I report a violation of an HR policy?
Violations can be reported to your manager, HR department, or through a confidential reporting system if available.
6)Can I suggest changes to an HR policy?
Employees can usually suggest changes through feedback mechanisms like surveys, suggestion boxes, or directly to HR.
7)Can HR policies change without notice?
Significant policy changes typically involve notice and communication to employees, though minor updates might not always be announced.
8)Who updates the HR policies, and how often?
The HR department updates policies, often annually or as needed due to legal changes or organizational updates.
9)In a case of workplace harassment, which HR policy should I apply/use?
The Anti-Harassment Policy and the Grievance Handling Policy apply in cases of workplace harassment.
10)How does the Remote Work Policy accommodate employees with disabilities?
It includes necessary accommodations and flexible arrangements to support employees with disabilities.
11)What HR policy covers data protection for employee information?
The Data and Information Security Policy covers the protection of employee personal and sensitive information.
12)Which HR policy should I refer to for understanding my employee's leave entitlements?
The Leave and Attendance Policy outlines leave entitlements and attendance requirements.
13) In a manufacturing setup, which HR policy is crucial for employee safety?
The Workplace Safety and Health Policy is crucial to address safety hazards.
14) After witnessing financial misconduct, which HR policy should be consulted?
The Whistleblower Policy provides guidelines for confidentially reporting misconduct.
15) Which HR policy outlines the process for employee promotions and appraisals?
The Performance Management and Appraisal Policy details the appraisal and promotion processes.
16) What HR policy should be referenced for expense reimbursements during business travel?
The Travel Policy includes guidelines for business travel expenses and reimbursements.
17) Which HR policy would cover the use of company equipment by my employees?
The Employee Laptop Policy or a broader IT and Equipment Use Policy would cover this.
18) How can grievances from remote employees be handled according to HR policies?
Through the Grievance Handling Policy, which includes provisions for remote submissions and virtual meetings.
19) What HR policy ensures diversity and inclusion within the workplace?
The Diversity and Inclusion Policy promotes a diverse and inclusive work environment.
Purpose of HR Policies in India
Conclusion
HR policies in India are super important for any company, including the sales department. They’re like the rules of the game that help everyone know how to play. This makes the workplace better for everyone, keeping things fair and clear. For sales folks, clear rules like commission policies can really help them stay focused and do their best.
In short, a good HR policies in India makes sure the company runs smoothly and everyone, from the top to the bottom, knows what’s expected. This is key for a company to do well and keep growing. To elevate your sales and HR strategies, check out Smart Sales Kit for a wide range of sales documents and HR policies in India designed to enhance team performance.
<a class=”buttonssk” href=”https://www.smartsaleskit.com/checkout/?add-to-cart=5832″>Buy Now @ ₹3,999 INR</a>